Programming Tricks
Julia
parentmodule: determine the package a function in Julia
originates from
names: Get a vector of the public names of a Module,
excluding deprecated names
undef: undef is a special marker used when constructing
arrays (including vectors) to indicate that the elements of the array
should not be initialized to any specific value.
collect: return an Array of all items in a collection or
iterator, collect(2:5), collect('B':'D'),
collect("HELLO")
!: a function naming convention to indicate that a
function mutates its arguments in place, meaning the changes will be
visible outside the function. When a function is designed to modify its
arguments, it is good practice to append a ! (exclamation
mark) to its name
eltype: To find the type of the elements that are
iterated over in a collection
typeof: To determine the specific type of any given
value
1 | pizza_tuple = ("hawaiian", 'S', 10.5) |
Any: It is used to construct a heterogeneous array that
can hold elements of any type, like
Any[1, "hello", 3.14]
^: Repeat a regex n times (s^n
is same with repeat(s, n)); Exponentiation operator
parse: convert a text string to anything else.
parse(Int, "42"), parse(Float64, "42")
String * : concatenate strings,
"The " * engine *
String $: string interpolation, use
$(variable) instead of $variable when there is
no whitespace that can clearly distinguish the variable name from the
surrounding text
vec: Reshape the array as a one-dimensional column
vector
pkg> dev|develop: add a local package, which not
initialized by git
load custom module:
1 | include("path/to/MyModule.jl") |
1 | include("path/to/MyModule.jl") |
1 | include("path/to/MyModule.jl") |
activate a Julia environment and execute a file using the command line
1 | julia --project=. your_script.jl |
The --project=. argument tells Julia to look for a
Project.toml and Manifest.toml file in the
current directory (indicated by .)
Instantiate the project
instantiate command to download and install all packages
and their dependencies listed in Project.toml (and
Manifest.toml if present)
create a new project
1 | $ julia |
]
1 | (@v1.12) pkg> generate MyNewProj |
;
1 | shell> cd MyNewProj/ |
]
1 | (@v1.12) pkg> activate . |
dictionary
1 | pizza = Dict("name" => "hawaiian", "size" => 'S', "price" => 10.5) |
A problem with using a dictionary is that it requires every value to be of the same type
1 | typeof(pizza) # Dict{String, Any} |
symbols
It is denoted by : (colon), followed by the name of
the symbol, built-in Julia type to represent identifiers
named tuples
1 | pizza = (name = "hawaiian", size = 'S', price = 10.5) |
A named tuple only allows you to use symbols as keys
All types of tuples are immutable, meaning you cannot change them
implicit naming from identifiers
1 | x = 0 |
composite type (struct) &
type annotation
:: is used to annotate variables and expressions with
their type. x::T means variable x should have
type T. It helps Julia figure out how many bytes are needed
to hold all fields in a struct
1 | struct Archer |
closure
varargs
"varargs" (variable arguments) refers to the ability of a function to
accept an arbitrary number of arguments. This is achieved using the
splat operator (...) in the function
definition.
1 | function my_sum(a, b, rest...) |
1 | my_sum(1, 2, 3, 4, 5) # 15 |
keyword arguments
a semicolon (;) separates positional arguments
from keyword arguments in the function signature. All arguments to the
right of the semicolon are treated as keyword arguments. They can
optionally have default values
views
A view is essentially a
pointer to a sub-section of another vector,
but not a standalone vector itself
1 | one2ten = collect(1:10); |
@viewsis a macro that converts sliced arrays into views (pointers are much cheaper than creating copies of arrays). For more information on how to use theviewsyntax correctly
semicolon after steprange
placing a semicolon ; after a step range expression
inside square brackets, e.g., [1:10;], changes the
resulting object from a UnitRange to a
Vector
1 | b = [1:2:10] # Vector{StepRange{Int64, Int64}} |
element-wise operations
Dot syntax for operators: For binary operators like
+, -, *, /,
^
Dot syntax for functions: For functions, the dot is placed after the function name.
Property destructuring
1 | julia> (; b, a) = (a=1, b=2, c=3) |
One-line functions
"one-line function" also known as the compact "assignment form"
1 | function_name(parameters) = expression |
Anonymous Functions (Lambda Functions)
functions without a name (parameters) -> expression,
often defined inline for use with higher-order functions like
map, filter, or reduce
1 | numbers = [1, 2, 3] |
using vs
import
that’s the difference between using and import - the former brings all exported names into scope, while the latter only brings NiceStuff (the module identifier) into scope.
[https://discourse.julialang.org/t/difference-between-include-use-and-import/65918/5]
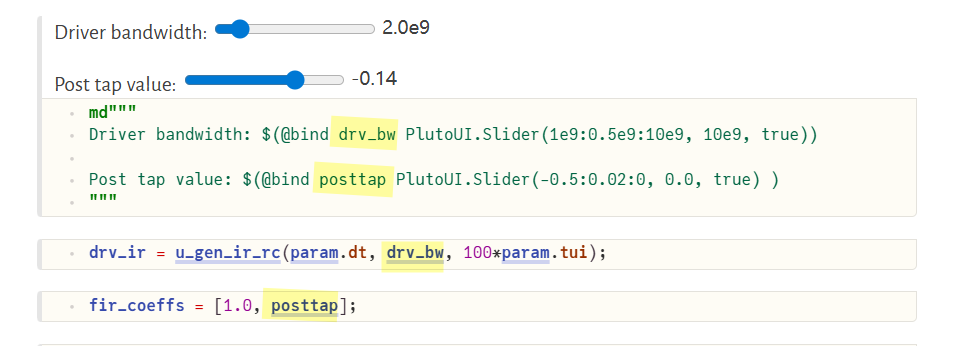
PlutoUI.Slider
C++ Conditional Compilation
Using g++ only
conditional.cpp
1 |
|
-DDEBUG args
1 | $ g++ -Wall -Wextra -Wconversion conditional.cpp -o conditional |
Using CMakeLists.txt add_definitions
1 | cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.2) |
without debug
1 | $ cmake .. |
with debug
1 | $ cmake -DDEBUG=ON .. |