UVM REG RALF & IP-XACT
uvm_reg_field
There are no properties for unused or reserved fields, and unlike register arrays
ralf
- bytes: the register size, default is N*8 > all field
1 | register CTRL { |
generated sv
1 | function void build(); |
uvm_reg_block
ralf
- bytes : bus width
1 | block vga_lcd { |
generated sv
1 | this.default_map = create_map("", 0, 4, UVM_LITTLE_ENDIAN, 0); |
1 | class ral_reg_CTRL extends uvm_reg; |
ralgen command
1 | ralgen -uvm -t dut_regmodel0 vga_lcd_env.ralf |
BYTE or HALFWORD access
User is verifying 32 bit registers and the design also allows the BYTE (8 bits) and HALFWORD (16 bits) accesses.
this is achieved by setting the bit_addressing=0 field in the uvm_reg_block::create_map function.
Using
create_mapinuvm_reg_block, you can change the type of addressing scheme you want to use; namely BYTE or HALFWORD.
create_map
1 | virtual function uvm_reg_map create_map( string name, |
Creates an address map with the specified name, then configures it with the following properties:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| base_addr | It is the base address for the map. All registers, memories, and sub-blocks within the map will be at offsets to this address. |
| n_bytes | It is the byte-width of the bus on which this map is used |
| endian | It is the endian format. See uvm_endianness_e for possible values. |
| byte_addressing | It specifies whether consecutive addresses referred are 1 byte apart (TRUE) or n_bytes apart (FALSE). Default is TRUE. |
- For HALFWORD addressing, you should call create_map the following way:
1 | default_map = create_map(get_name(), 0, 2, UVM_LITTLE_ENDIAN, 0); // 32 bit registers offset are 0x00, 0x02, 0x04 |
- For WORD addressing
1 | default_map = create_map(get_name(), 0, 4, UVM_LITTLE_ENDIAN, 0); // 32 bit registers offset are 0x00, 0x01, 0x02 |
- For BYTE addressing (default) :
1 | default_map = create_map(get_name(), 0, 4, UVM_LITTLE_ENDIAN, 1); // 32 bit registers offset are 0x00, 0x04, 0x08 |
- BYTE width and byte addressing
1 | default_map = create_map(get_name(), 0, 1, UVM_LITTLE_ENDIAN, 1); // 32 bit registers offset are 0x00, 0x04, 0x08 |
uvm_reg_block::create_map
Create an address map in this block
n_bytes - the byte-width of the bus on which this map is used
byte_addressing - specifies whether consecutive addresses refer are 1 byte apart (TRUE) or
n_bytesapart (FALSE). Default is TRUE.
1 | function uvm_reg_map uvm_reg_block::create_map(string name, |
uvm_reg_map::add_reg
The register is located at the specified address offset from this maps configured base address.
The number of consecutive physical addresses occupied by the register depends on the width of the register and the number of bytes in the physical interface corresponding to this address map.
If unmapped is TRUE, the register does not occupy any physical addresses and the base address is ignored. Unmapped registers require a user-defined frontdoor to be specified.
1 | function void uvm_reg_map::add_reg(uvm_reg rg, |
Register Defines
`UVM_REG_ADDR_WIDTH
Maximum address width in bits
Default value is 64. Used to define the
type.
1 |
`UVM_REG_DATA_WIDTH
Maximum data width in bits
Default value is 64. Used to define the
type.
1 |
Generic RALF Features and IP-XACT Mapping
field

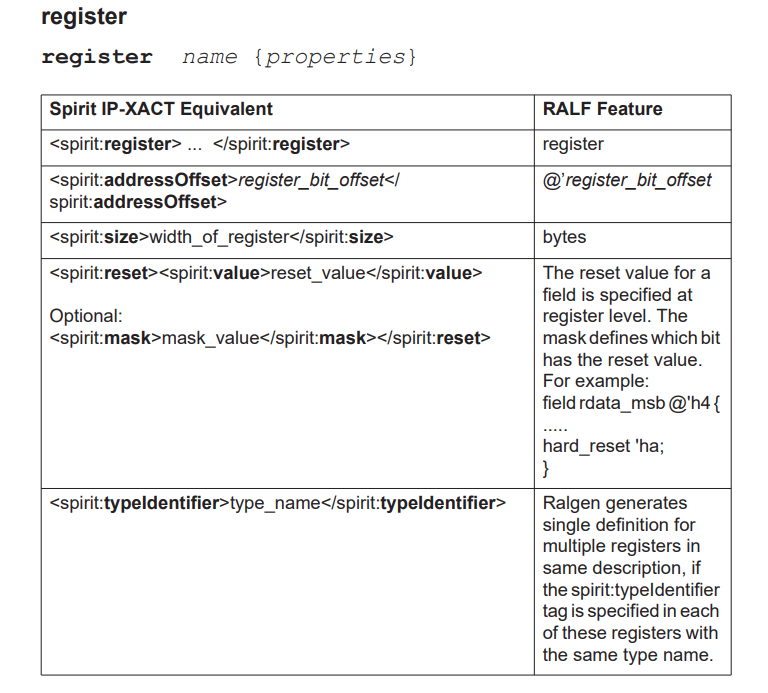
register
addressOffset
a register has an addressOffset that describes the
location of the register expressed in addressUnitBits as
offset to the starting address of the containing
addressBlock or the containing
registerFile
addressUnitBits
The addressUnitBits element describes the number of bits
of an address increment between two consecutive addressable
units in the addressSpace. If
addressUnitBits is not described, then its value
defaults to 8, indicating a
byte-addressable addressSpace
block

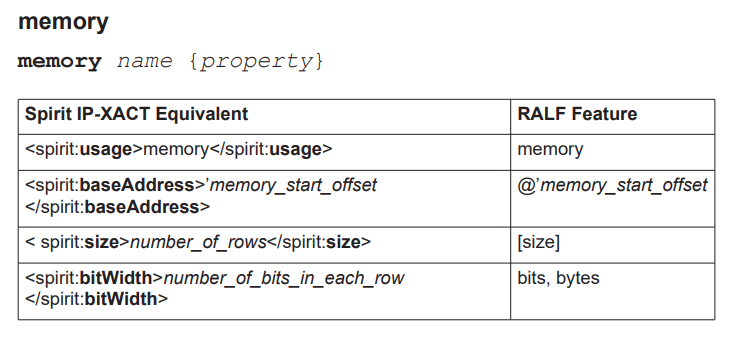
memory
Reference
UVM Register Abstraction Layer Generator User Guide, S-2021.09-SP1, December 2021