Functional Coverage Modeling
Coverage Options
- Explicit (user defined)
- Fully and clearly expressed within sources
- Sequence and temporal coverage using assertions
- Data-oriented coverage using
covergroup
- Planned and defined by the verification team
- Fully and clearly expressed within sources
- Implicit
- Derived or computed from source
- Code coverage measured by the simulator
- May be defined outside the verification team
- May be implied by the verification interface
- e.g., an industry standard protocol
- Derived or computed from source
Explicit Coverage in Systemverilog
Assertions for control-oriented coverage
- Defined as procedural statements
- CANNOT be defined in a class
1 | property req_gnt (cyc); |
Control-oriented coverage uses SystemVerilog Assertion (SVA) syntax and the cover directive. It is used to cover sequences of signal values over time. Assertions cannot be declared or "covered" in a class declaration, so their use in an UVM verification environment is restricted to interface only
Covergroup for data-oriented coverage
- CAN be declared as a class member and created in class constructor
- Used in interface and module UVCs
1 | covergroup cg @(posedge clk); |
Data-oriented coverage uses the
covergroupconstruct. Covergroups can be declared and created in classes, therefore they are essential for explicit coverage in a UVM verification environment.
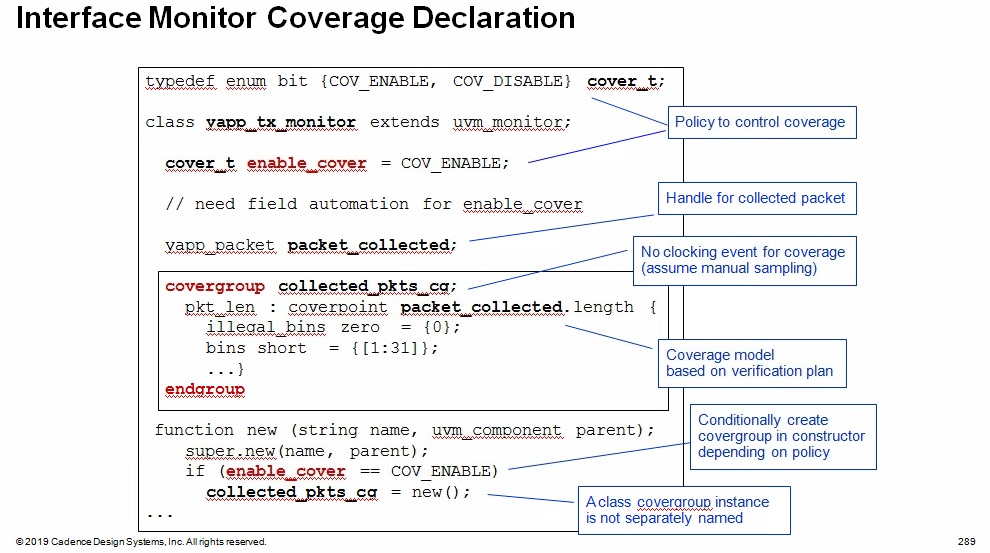
Interface Monitor Coverage
covergroup new constructor is called
directly off the declaration of the covergroup, it does
not have a separate instance name
1 | collected_pkts_cq = new(); |
The covergroup instance must be created in the class
constructor, not a UVM build_phase or other phase
method
1 | class yapp_tx_monitor extends uvm_monitor; |
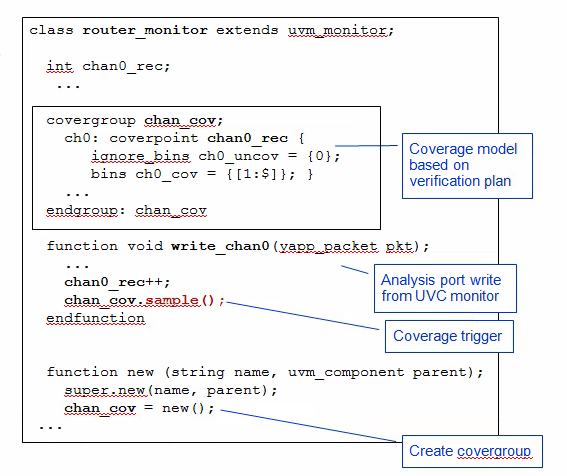
Module UVC Coverage
Typical module UVC coverage:
- Routing - packets flow from input ports to all legal outputs
- latency - all packets received within speicied delay
The module UVC monitor receives data from the interface monitors via analysis ports, so the implementation of the analysis write function is a convenient place to put coverage code