VLSI Digital Signal Processing
Single-Pole LPF Algorithms
Neil Robertson, Model a Sigma-Delta DAC Plus RC Filter [https://www.dsprelated.com/showarticle/1642.php]
Jason Sachs, Ten Little Algorithms, Part 2: The Single-Pole Low-Pass Filter [https://www.embeddedrelated.com/showarticle/779.php]
—. Return of the Delta-Sigma Modulators, Part 1: Modulation [https://www.dsprelated.com/showarticle/1517/return-of-the-delta-sigma-modulators-part-1-modulation]
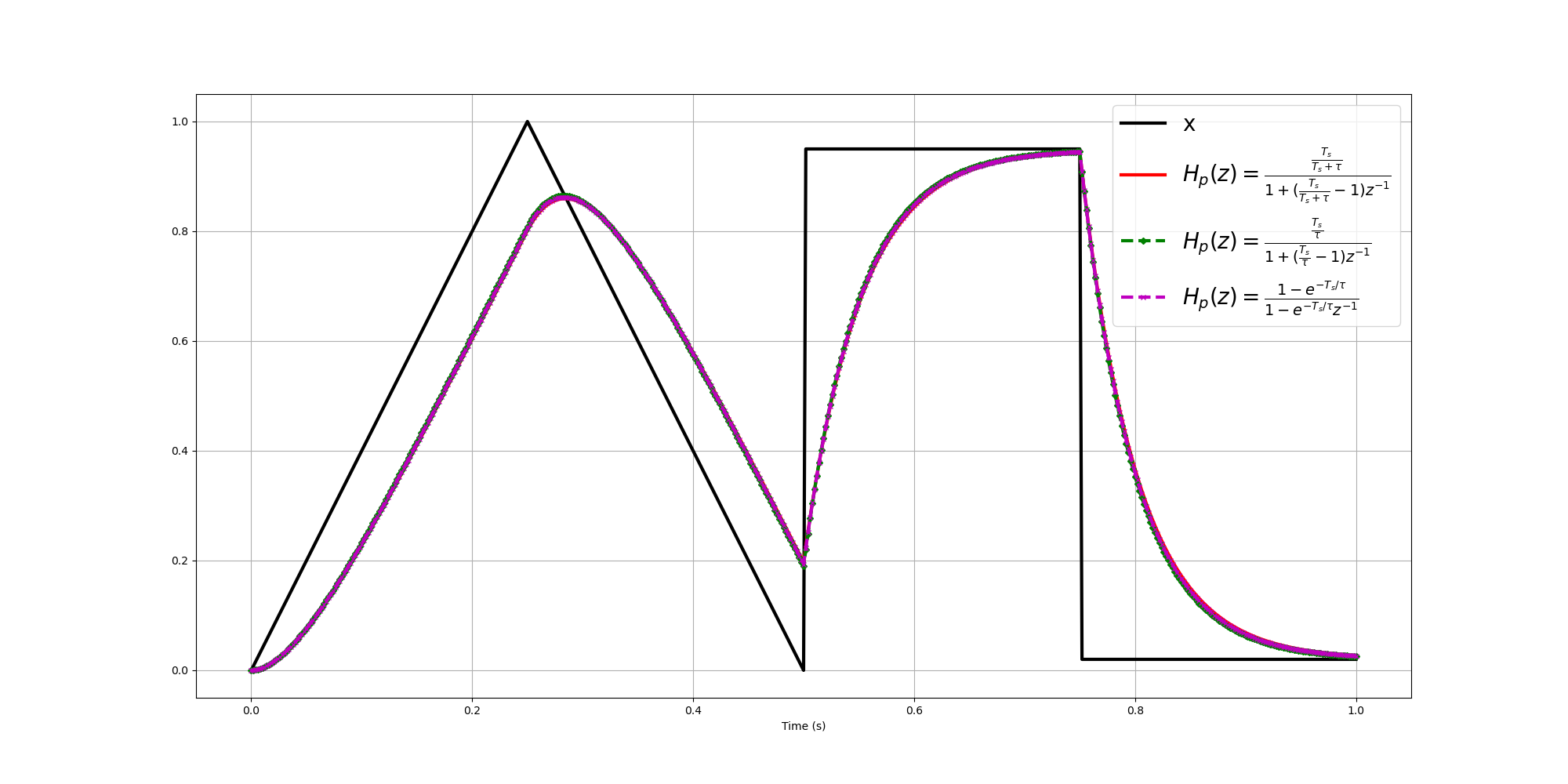
Derivatives Approximation (\(H_p(s)=\frac{1}{s\tau +1}\))
\[\begin{align} H_p(z)&=\frac{\frac{T_s}{T_s+\tau}}{1+(\frac{T_s}{T_s+\tau}-1)z^{-1}}\tag{EQ-0}\\ H_p(z)&=\frac{\frac{T_s}{\tau}}{1+(\frac{T_s}{\tau}-1)z^{-1}}\tag{EQ-1} \end{align}\]
Matched z-Transform (Root Matching) \[ H_p(z)=\frac{1-e^{-T_s/\tau}}{1-e^{-T_s/\tau}z^{-1}}\tag{EQ-2} \] EQ-2 is connected with EQ-1 by \(1 - e^{-\Delta t/\tau} \approx \frac{\Delta t}{\tau}\)
1 | import numpy as np |
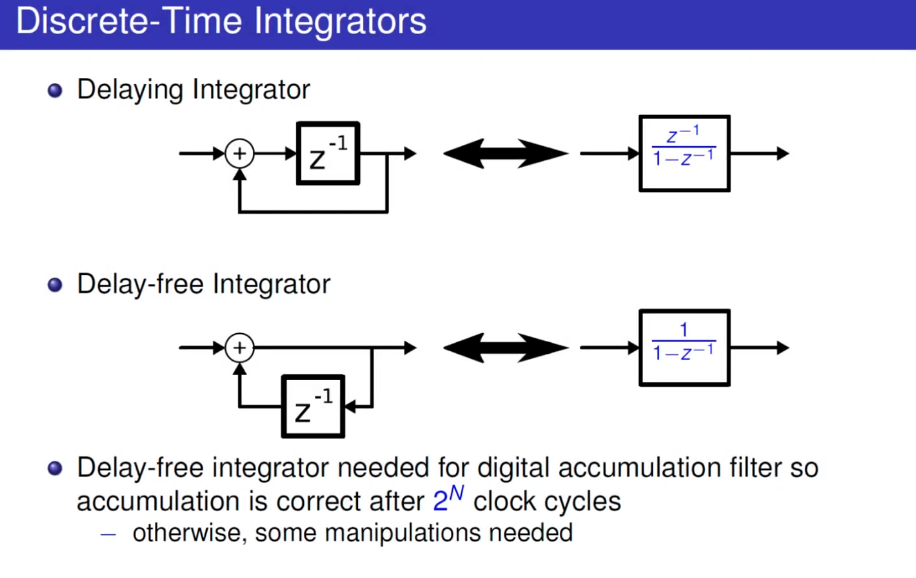
Discrete-Time Integrators
Qasim Chaudhari. Discrete-Time Integrators [https://wirelesspi.com/discrete-time-integrators/]
David Johns (University of Toronto) "Oversampled Data Converters" Course (2019) [https://youtu.be/qIJ2LORYmyA?si=_pGb18rhsMUZ-lAf]
Delaying Integrator
Delay-free Integrator
Discrete-Time Differentiator
Qasim Chaudhari. Design of a Discrete-Time Differentiator [https://wirelesspi.com/design-of-a-discrete-time-differentiator/]
TODO 📅
Accumulate-and-dump (AAD) decimator
accumulating the input for \(N\) cycles and then latching the result and resetting the integrator
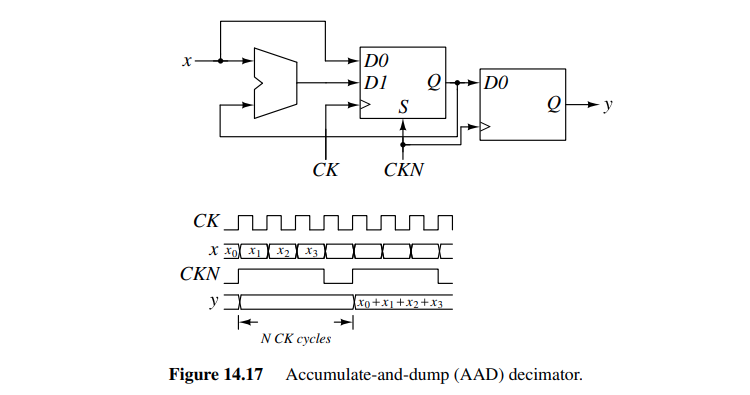
It adds up \(N\) succeeding input samples at rate \(1/T\) and delivers their sum in a single sample at the output. Therefore, the process comprises a filter (in the accumulation) and a down-sampler (in the dump)
Moving Average and CIC Filters
An Intuitive Look at Moving Average and CIC Filters [web, code]
A Beginner's Guide To Cascaded Integrator-Comb (CIC) Filters [https://www.dsprelated.com/showarticle/1337.php]
TODO 📅
Cascaded Integrator-Comb (CIC) filter
Let’s focus on decimation: if we decimate by a factor 4, we simply retain one output sample out of every 4 input samples.
In the example below, the downsampler at the right drops those 3 samples out of 4, and the output rate, \(y^\prime(n)\), is one fourth of the input rate \(x(n)\):
\[\begin{align}
Y(z) &= X(z)\frac{1-z^{-4}}{1-z^{-1}} \\
Y^\prime(\xi) &= \frac{1}{4}Y(\xi^{1/4}) =
\frac{1}{4}X(\xi^{1/4})\frac{1-\xi^{-1}}{1-\xi^{-1/4}}
\end{align}\]
with \(z=e^{j\Omega/f_s}\) and \(\xi =z^4\), we have \[ Y^\prime(z) = \frac{1}{4}X(z)\frac{1-z^{-4}}{1-z^{-1}} \]
But if we're going to be throwing away 75% of the calculated values, can't we just move the downsampler from the end of the pipeline to somewhere in the middle? Right between the integrator stage and the comb stage? That answer is yes, but to keep the math working, we also need to divide the number of delay elements in the comb stage by the decimation rate:
\[\begin{align} A(z) &= X(z)\frac{1}{1-z^{-1}} \\ A^\prime(\xi) &= \frac{1}{4}A(\xi^{1/4}) = \frac{1}{4}X(\xi^{1/4})\frac{1}{1-\xi^{-1/4}} \\ Y^\prime(\xi) &= A^\prime(\xi) (1-\xi^{-1}) = \frac{1}{4}X(\xi^{1/4})\frac{1-\xi^{-1}}{1-\xi^{-1/4}} \end{align}\]
with \(z=e^{j\Omega/f_s}\) and \(\xi =z^4\), we have \[ Y^\prime(z) = \frac{1}{4}X(z)\frac{1-z^{-4}}{1-z^{-1}} \]
And we can do this just the same with cascaded sections (without downsampler or updampler) where integrators and combs have been grouped
- for decimation, the integrators come first and the combs second with the downsampler in between
- For interpolation, the reverse is true
- the incoming sample rate is fraction of the outgoing sample rate, the combs must come first and the interpolators second
Tom Verbeure. An Intuitive Look at Moving Average and CIC Filters [https://tomverbeure.github.io/2020/09/30/Moving-Average-and-CIC-Filters.html]
—. Half-Band Filters, a Workhorse of Decimation Filters [https://tomverbeure.github.io/2020/12/15/Half-Band-Filters-A-Workhorse-of-Decimation-Filters.html]
—. Design of a Multi-Stage PDM to PCM Decimation Pipeline [https://tomverbeure.github.io/2020/12/20/Design-of-a-Multi-Stage-PDM-to-PCM-Decimation-Pipeline.html]
Arash Loloee, Ph.D. Exploring Decimation Filters [https://www.highfrequencyelectronics.com/Archives/Nov13/1311_HFE_decimationFilters.pdf]
Rick Lyons. A Beginner's Guide To Cascaded Integrator-Comb (CIC) Filters [https://www.dsprelated.com/showarticle/1337.php]
reference
Jabbour, Chadi, etc.. "Digitally enhanced mixed signal systems." IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS). 2019.
Sen M. Kuo. Real-Time Digital Signal Processing: Fundamentals, Implementations and Applications, 3rd Edition. John Wiley & Sons 2013
Taylor, Fred. Digital filters: principles and applications with MATLAB. John Wiley & Sons, 2011
Kuo, Sen-Maw. (2013) Real-Time Digital Signal Processing: Implementations and Applications 3rd [pdf]
D. Markovic and R. W. Brodersen, DSP Architecture Design Essentials, Springer, 2012.
Bevan Baas, EEC281 VLSI Digital Signal Processing, [https://www.ece.ucdavis.edu/~bbaas/281/]
Mark Horowitz. EE371: Advanced VLSI Circuit Design Spring 2006-2007 [https://web.stanford.edu/class/archive/ee/ee371/ee371.1066/]
謝秉璇. 2019 積體電路設計導論 [link]
Tinoosh Mohsenin. CMPE 691: Digital Signal Processing Hardware Implementation [https://userpages.cs.umbc.edu/tinoosh/cmpe691/]
Keshab K. Parhi [http://www.ece.umn.edu/users/parhi/]
Qasim Chaudhari. FIR vs IIR Filters – A Practical Comparison [https://wirelesspi.com/fir-vs-iir-filters-a-practical-comparison/]
—. Finite Impulse Response (FIR) Filters [https://wirelesspi.com/finite-impulse-response-fir-filters/]
—. Why FIR Filters have Linear Phase [https://wirelesspi.com/why-fir-filters-have-linear-phase/]
—. Moving Average Filter [https://wirelesspi.com/moving-average-filter/]
—. Cascaded Integrator Comb (CIC) Filters – A Staircase of DSP. [https://wirelesspi.com/cascaded-integrator-comb-cic-filters-a-staircase-of-dsp/]
Jason Sachs. Understanding and Preventing Overflow (I Had Too Much to Add Last Night) [https://www.embeddedrelated.com/showarticle/532.php]
—. Round Round Get Around: Why Fixed-Point Right-Shifts Are Just Fine [https://www.embeddedrelated.com/showarticle/1015.php]
—. How to Build a Fixed-Point PI Controller That Just Works: Part I [https://www.embeddedrelated.com/showarticle/121.php]
—. How to Build a Fixed-Point PI Controller That Just Works: Part II [https://www.embeddedrelated.com/showarticle/123.php]