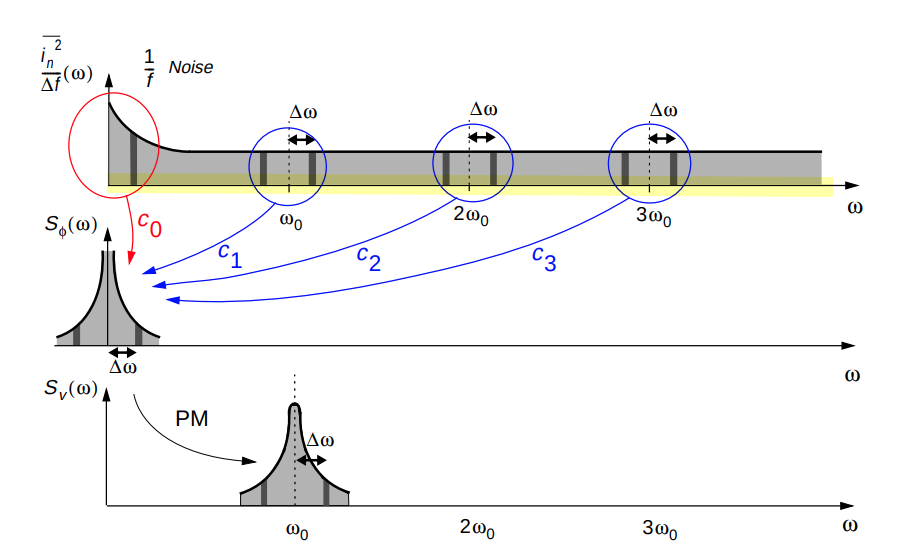
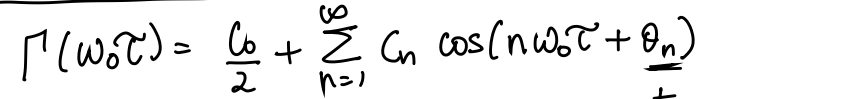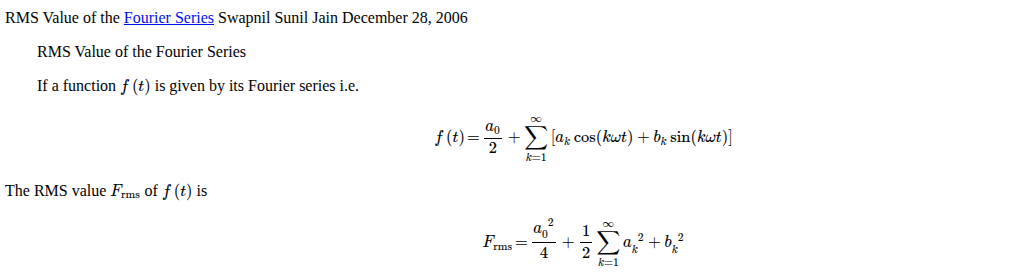Oscillators in Action
Leeson's Model - LTI
M.H. Perrott [https://www.cppsim.com/PLL_Lectures/day2_am.pdf]
Leeson's model is outcome of linearized VCO noise analysis

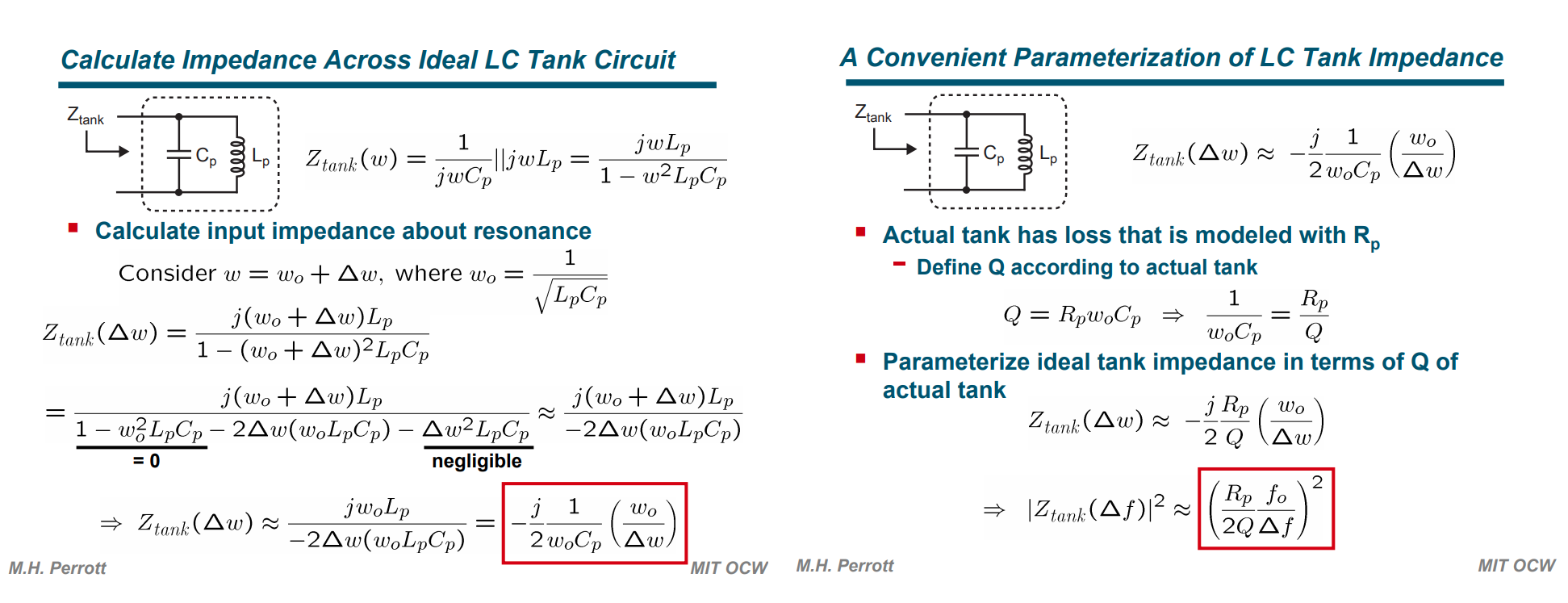
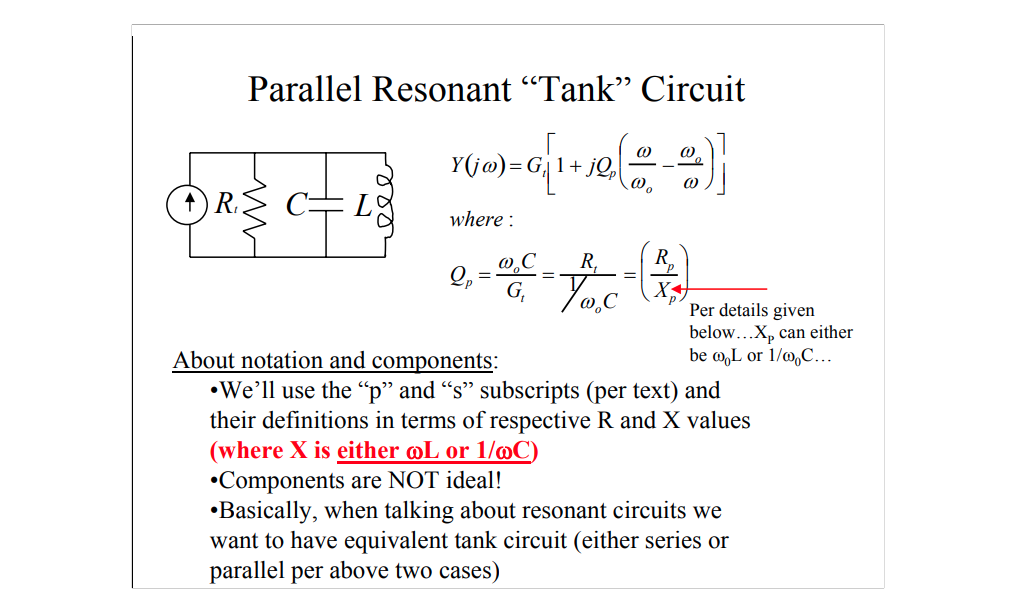
\[ Q = R_p\omega_0 C_p = \frac{R_p}{\omega_0 L} \]
where \(\omega_0 = \frac{1}{\sqrt{L_pC_p}}\)
[https://stanford.edu/class/ee133/handouts/lecturenotes/lecture5_tank.pdf]
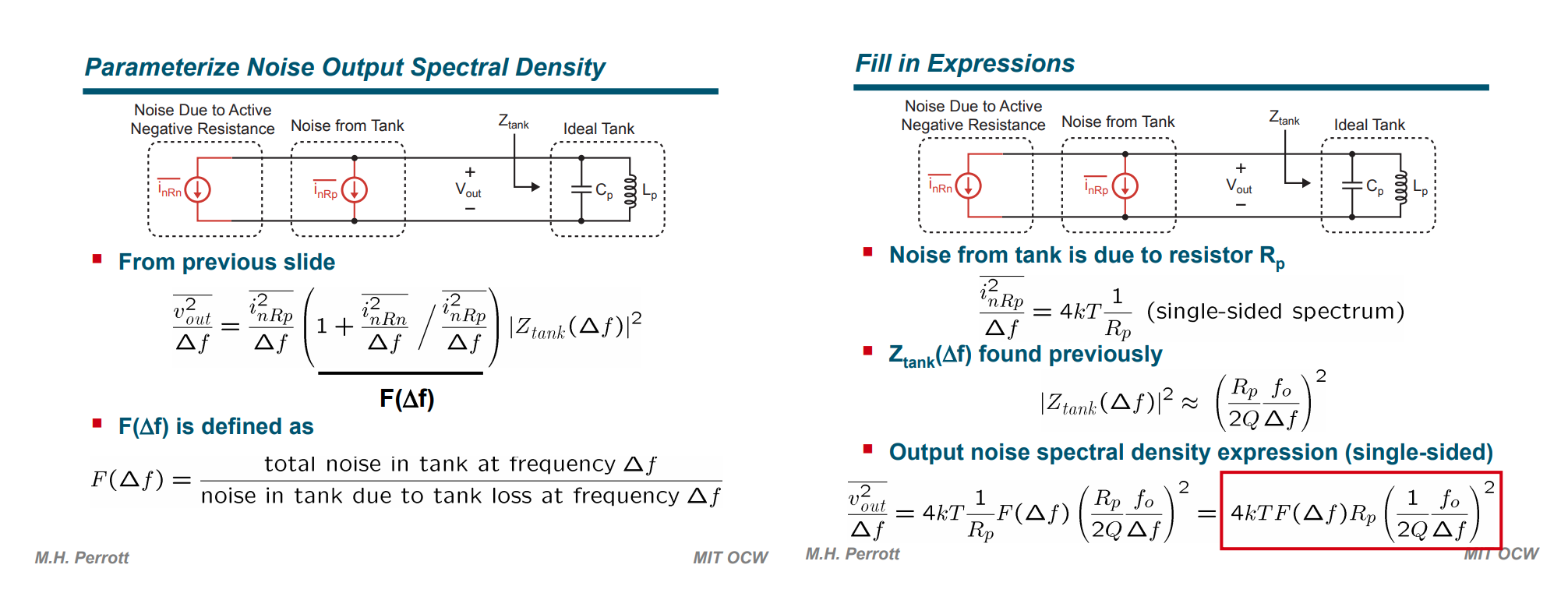
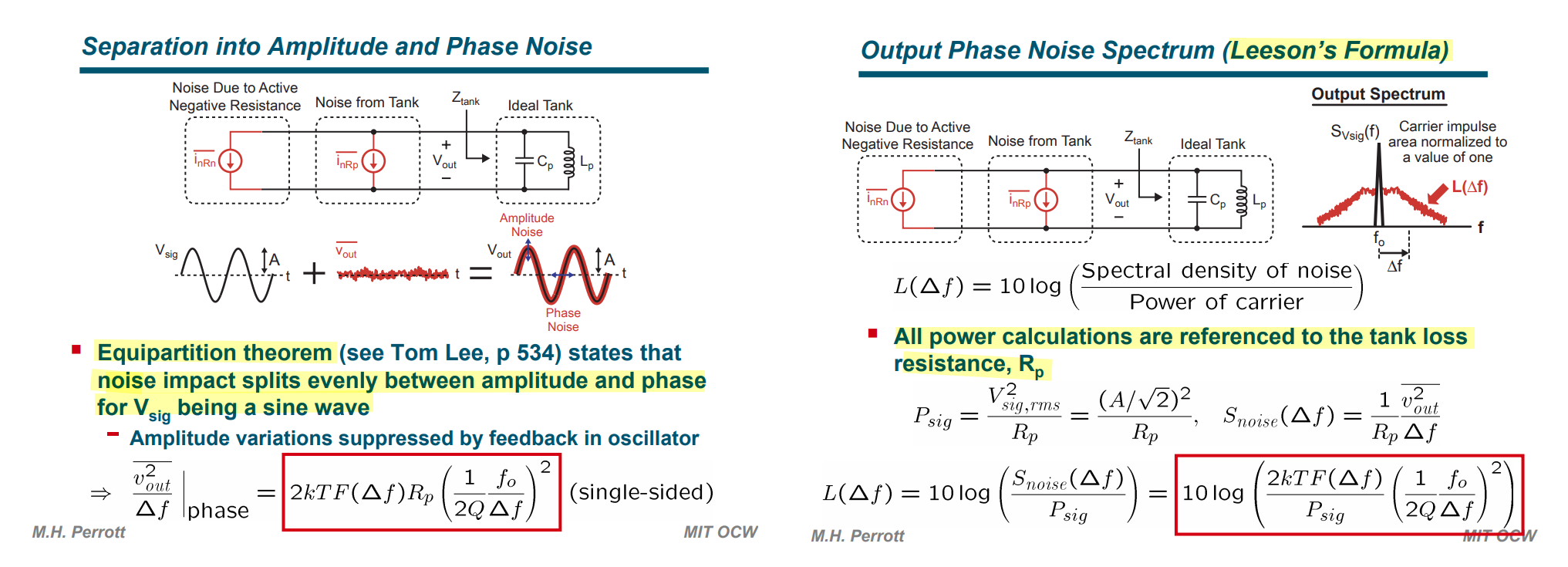
Carlo Samori ISSCC2016 T1: Understanding Phase Noise in LC VCOs

Leeson's limitations

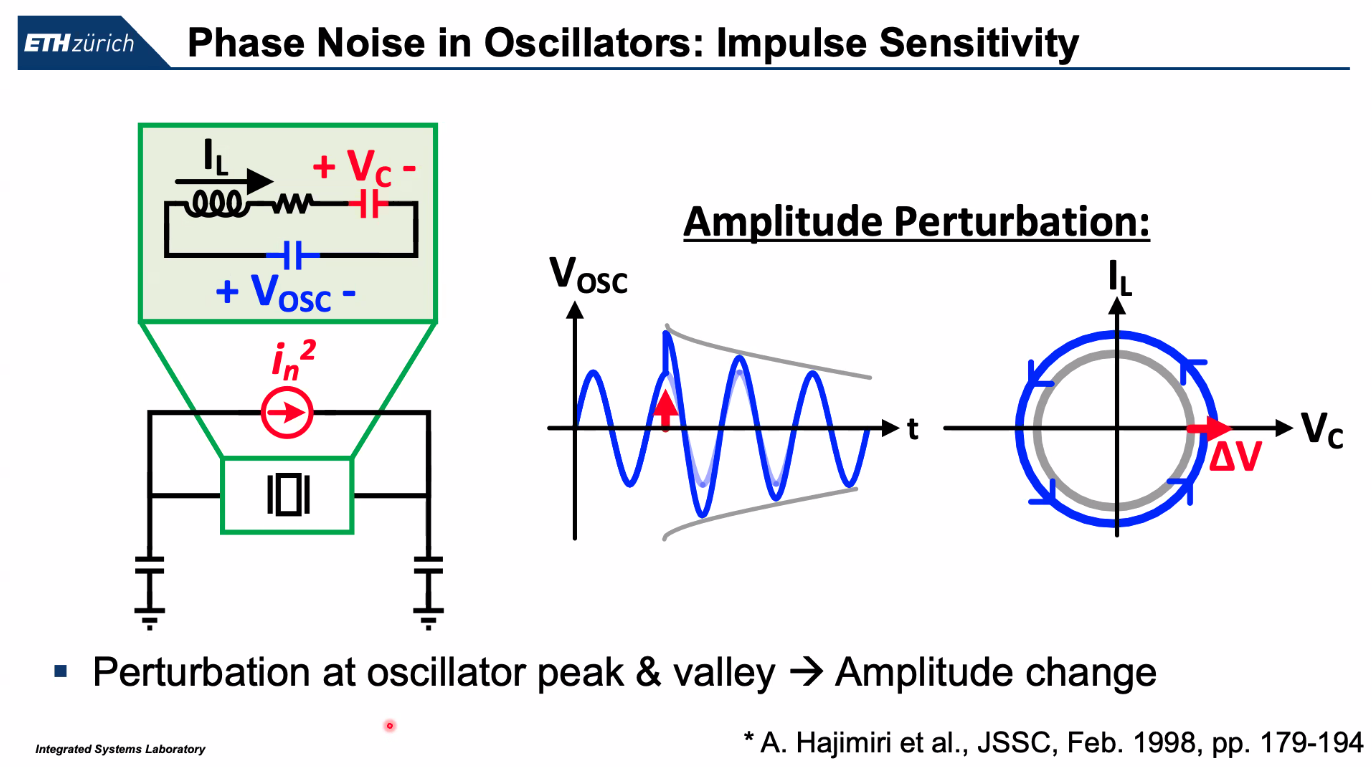
Hajimiri's Model- LTV ISF

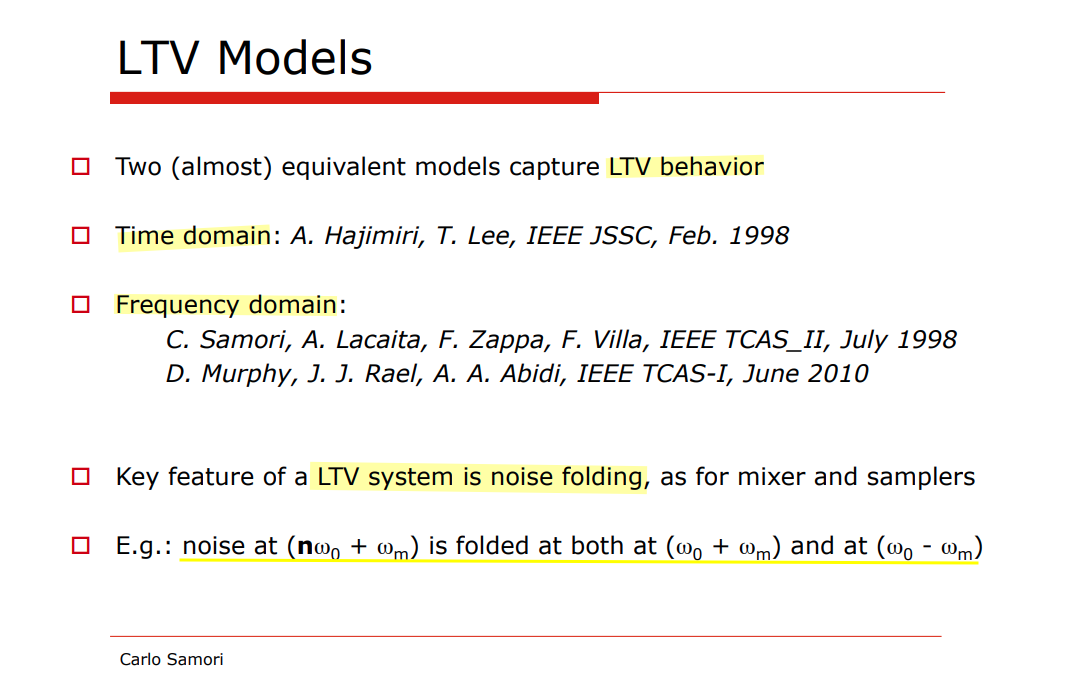
ISF model
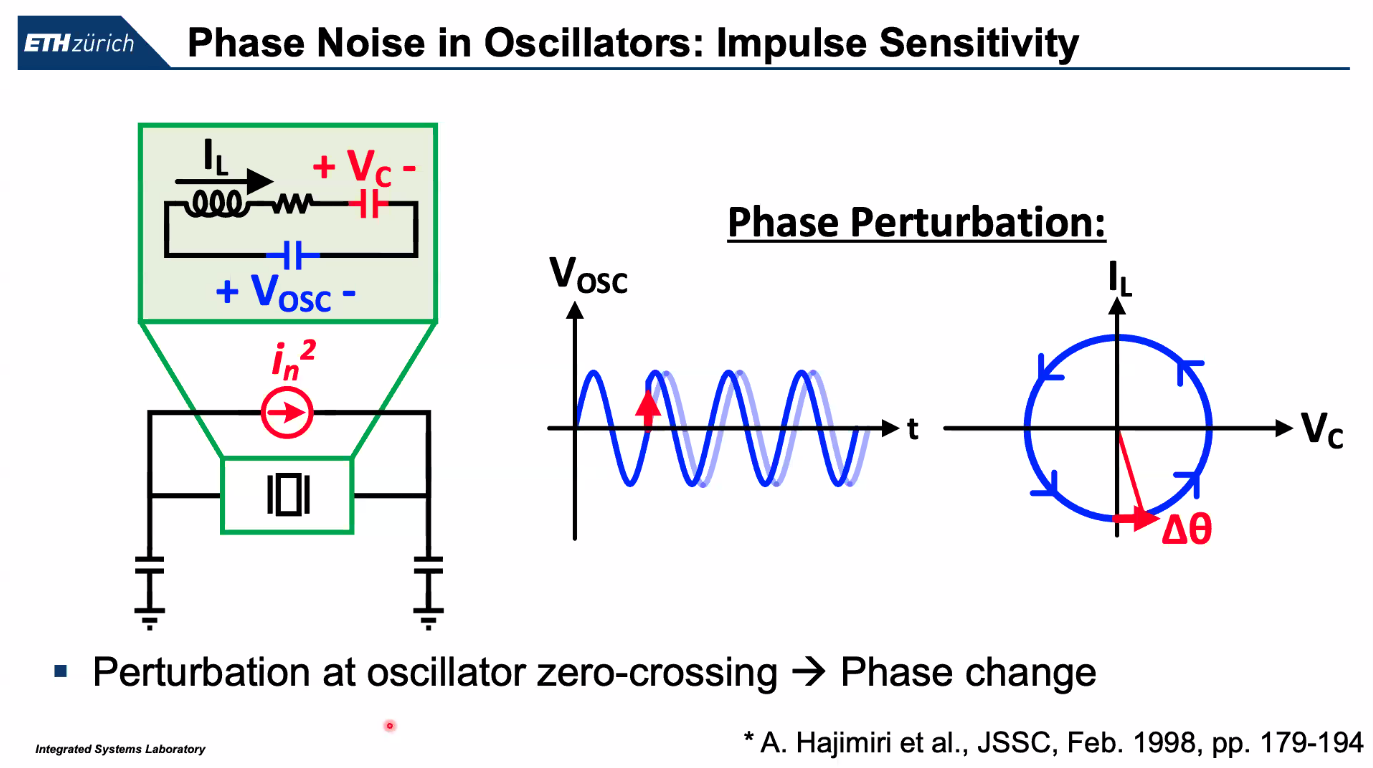
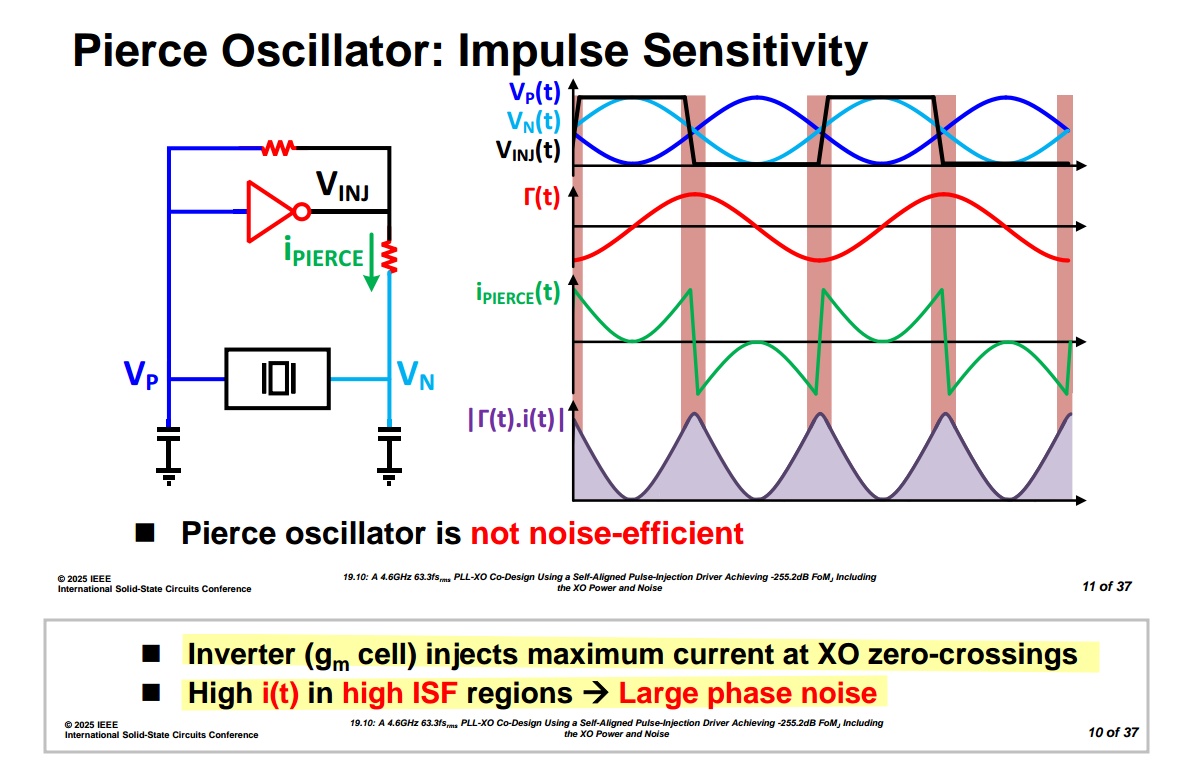
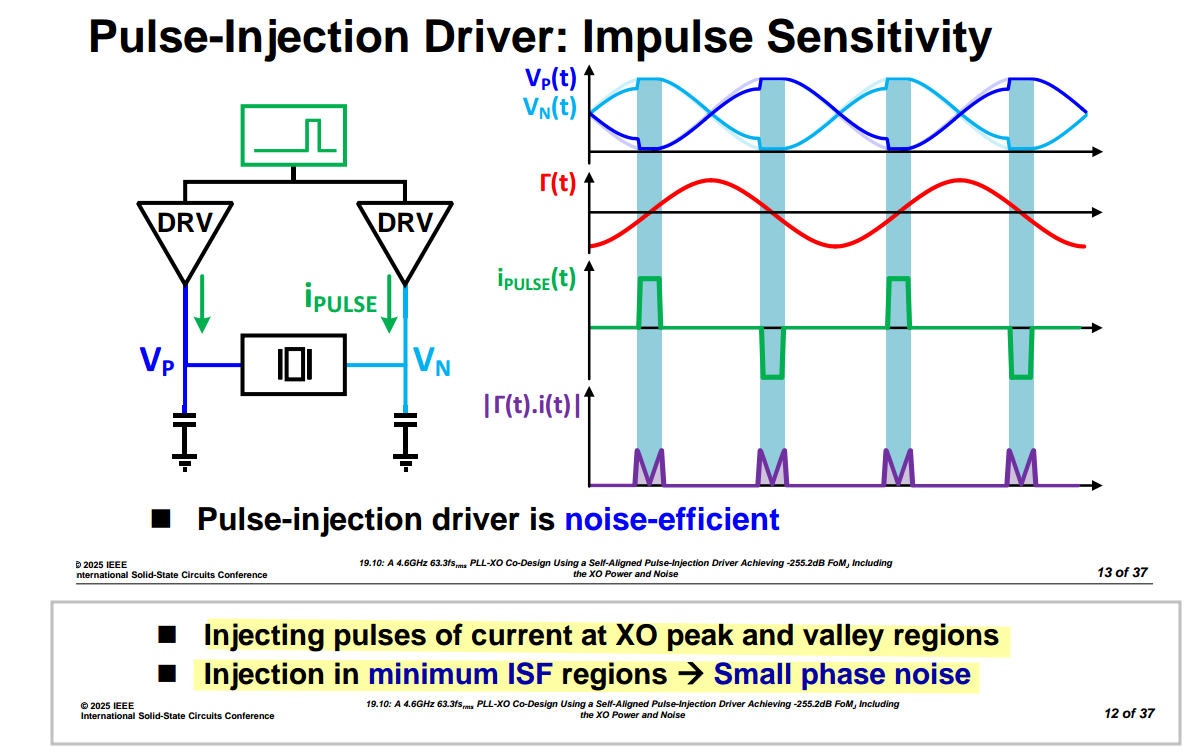
C. Livanelioglu, L. He, J. Gong, S. Arjmandpour, G. Atzeni and T. Jang, "19.10 A 4.6GHz 63.3fsrms PLL-XO Co-Design Using a Self-Aligned Pulse-Injection Driver Achieving −255.2dB FoMJ Including the XO Power and Noise," 2025 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference (ISSCC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 2025
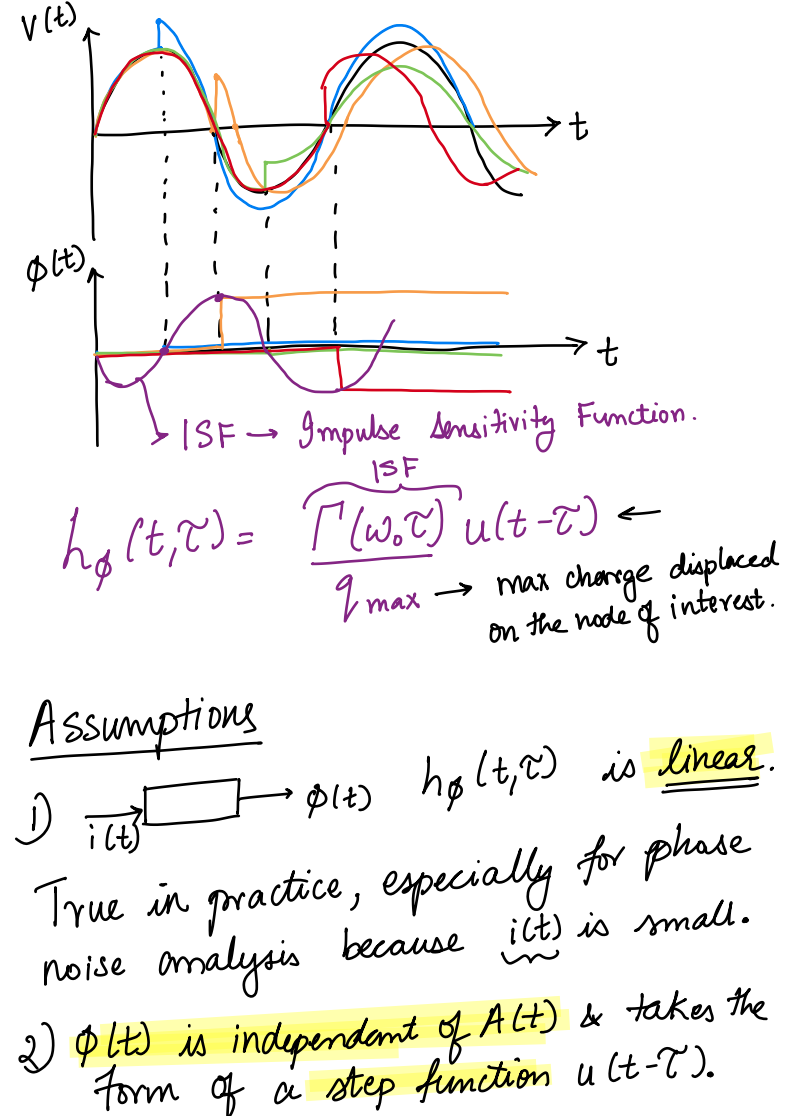
[https://adityamuppala.github.io/assets/Notes_YouTube/Oscillators_ISF_model.pdf]
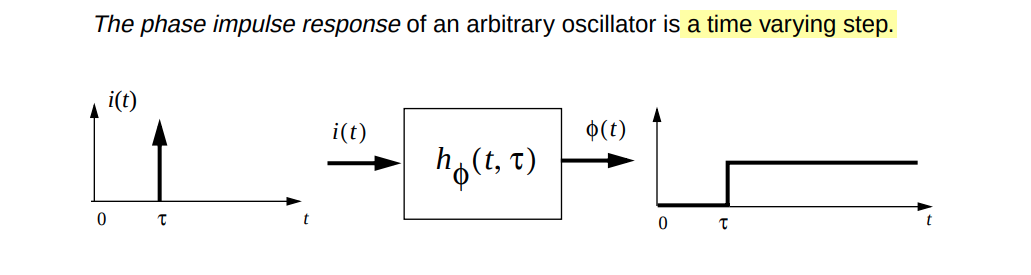
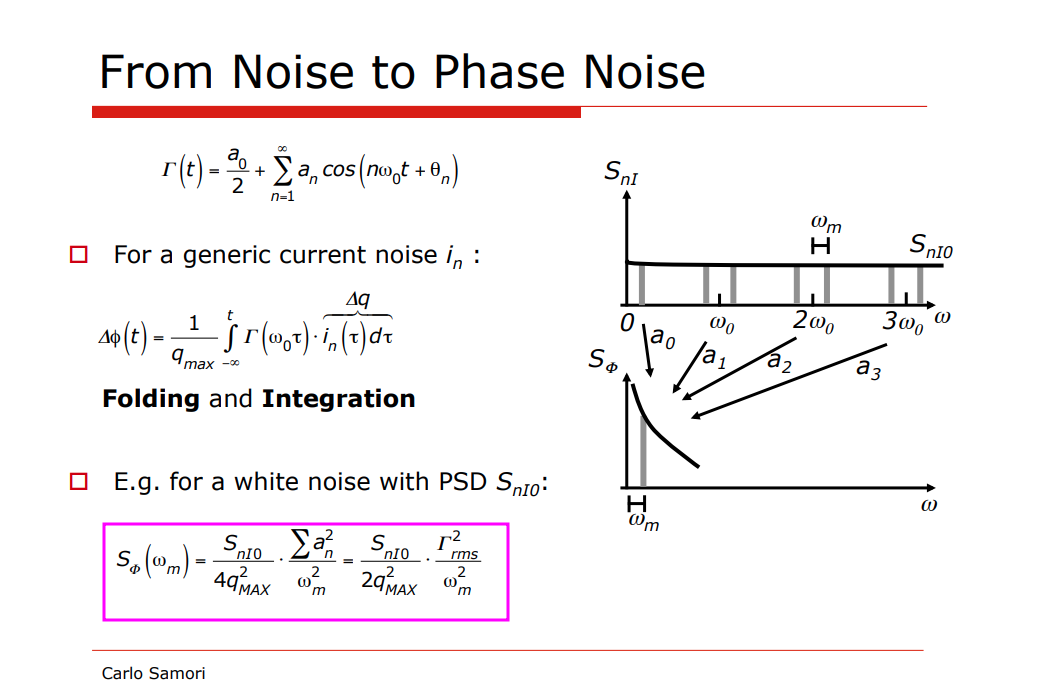
Periodic ISF: Noise Folding
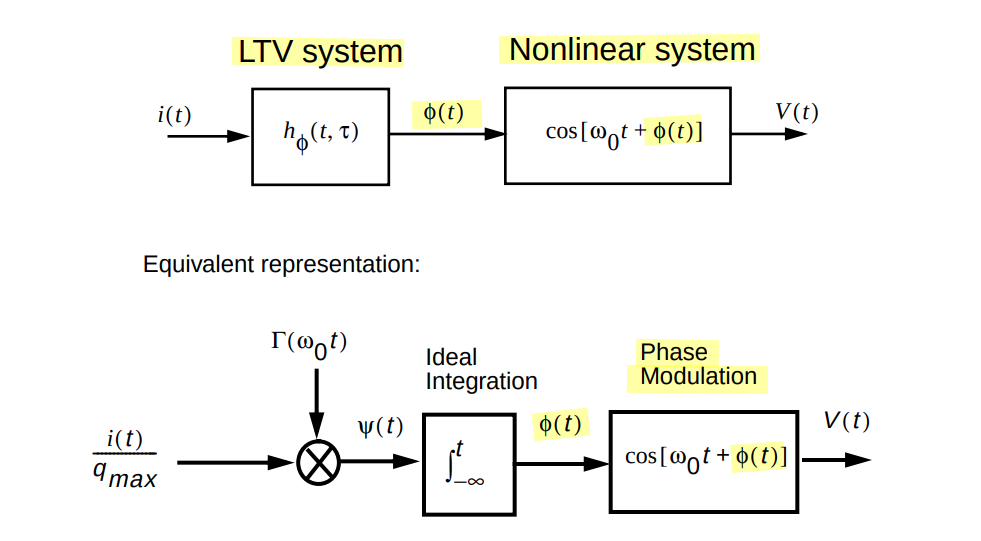
When performing the phase noise computation integral, there will be a negligible contribution from all terms, other than \(n=m\)
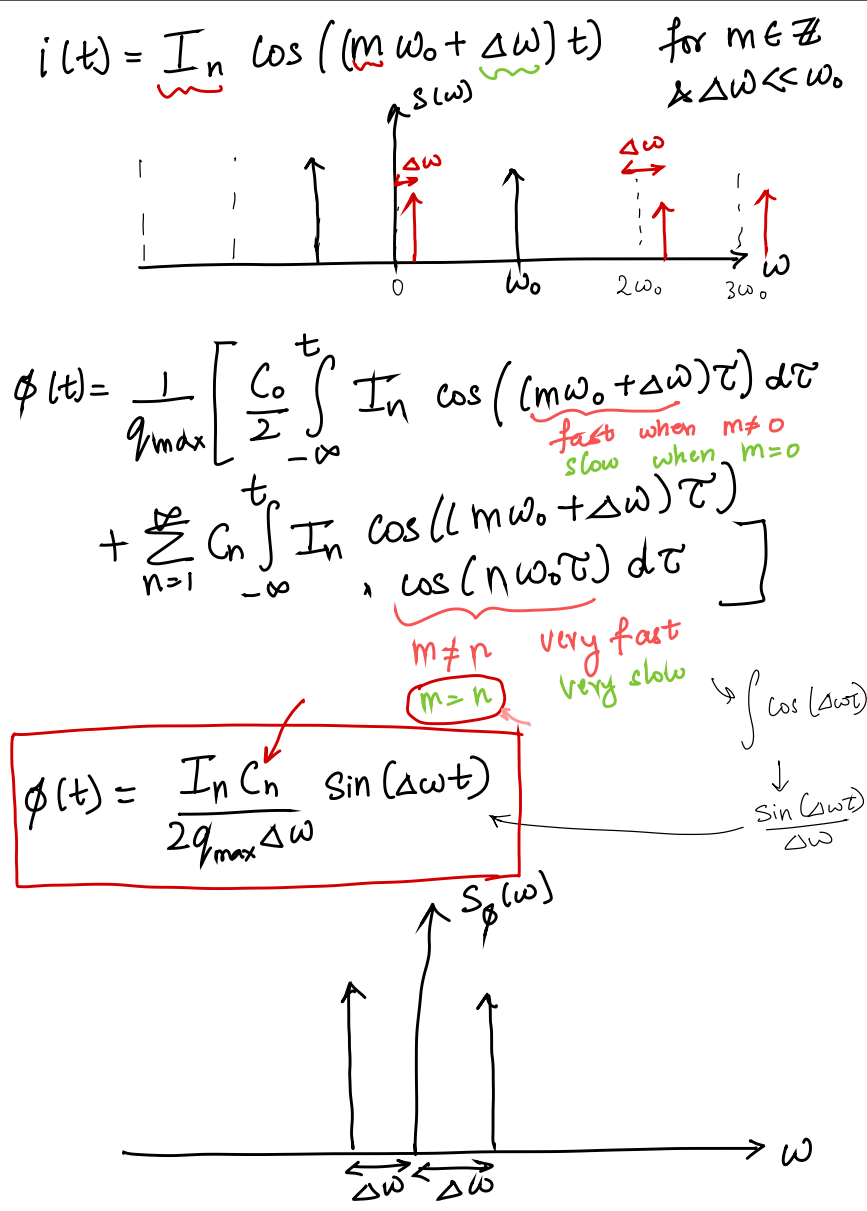
Given \(i(t) = I_m \cos[(m\omega_0 +\Delta \omega)t]\),
\[\begin{align} \phi(t) &= \frac{1}{q_\text{max}}\left[\frac{C_0}{2}\int_{-\infty}^t I_m\cos((m\omega_0 +\Delta \omega)\tau)d\tau + \sum_{n=1}^\infty C_n\int_{-\infty}^t I_m\cos((m\omega_0 +\Delta \omega)\tau)\cos(n\omega_0\tau)d\tau\right] \\ &= \frac{I_m}{q_\text{max}}\left[\frac{C_0}{2}\int_{-\infty}^t \cos((m\omega_0 +\Delta \omega)\tau)d\tau + \sum_{n=1}^\infty C_n\int_{-\infty}^t \frac{\cos((m\omega_0 + \Delta \omega+ n\omega_0)\tau)+ \cos((m\omega_0+\Delta \omega - n\omega_0)\tau)}{2}d\tau\right] \end{align}\]
If \(m=0\) \[ \phi(t) \approx \frac{I_0C_0}{2q_\text{max}\Delta \omega}\sin(\Delta\omega t) \] If \(m\neq 0\) and \(m=n\) \[ \phi(t) \approx \frac{I_mC_m}{2q_\text{max}\Delta \omega}\sin(\Delta\omega t) \]
\(m\omega_0 +\Delta \omega \ge 0\)

A. Hajimiri and T. H. Lee, "A general theory of phase noise in electrical oscillators," in IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, vol. 33, no. 2, pp. 179-194, Feb. 1998 [pdf]
Corrections to "A General Theory of Phase Noise in Electrical Oscillators"
A. Hajimiri and T. H. Lee, "Corrections to "A General Theory of Phase Noise in Electrical Oscillators"," in IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, vol. 33, no. 6, pp. 928-928, June 1998 [https://sci-hub.se/10.1109/4.678662]
Ali Hajimiri. Phase Noise in Oscillators [http://www-smirc.stanford.edu/papers/Orals98s-ali.pdf]
L. Lu, Z. Tang, P. Andreani, A. Mazzanti and A. Hajimiri, "Comments on “Comments on “A General Theory of Phase Noise in Electrical Oscillators””," in IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, vol. 43, no. 9, pp. 2170-2170, Sept. 2008 [https://sci-hub.se/10.1109/JSSC.2008.2005028]

Given \(i(t) = I_m \cos[(m\omega_0 - \Delta \omega)t]\) and \(m \ge 1\)
\[\begin{align} \phi(t) &= \frac{1}{q_\text{max}}\left[\frac{C_0}{2}\int_{-\infty}^t I_m\cos((m\omega_0 -\Delta \omega)\tau)d\tau + \sum_{n=1}^\infty C_n\int_{-\infty}^t I_m\cos((m\omega_0 -\Delta \omega)\tau)\cos(n\omega_0\tau)d\tau\right] \\ &= \frac{I_m}{q_\text{max}}\left[\frac{C_0}{2}\int_{-\infty}^t \cos((m\omega_0 -\Delta \omega)\tau)d\tau + \sum_{n=1}^\infty C_n\int_{-\infty}^t \frac{\cos((m\omega_0 - \Delta \omega+ n\omega_0)\tau)+ \cos((m\omega_0-\Delta \omega - n\omega_0)\tau)}{2}d\tau\right] \end{align}\]
If \(m\ge 1\) and \(m=n\) \[ \phi(t) \approx \frac{I_mC_m}{2q_\text{max}\Delta \omega}\sin(\Delta\omega t) \] That is
| \(m = 0\) | \(m\gt 0\) & \(m\omega_0+\Delta \omega\) | \(m\gt 0\) & \(m\omega_0-\Delta \omega\) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| \(\phi(t)\) | \(\frac{I_0C_0}{2q_\text{max}\Delta \omega}\sin(\Delta\omega t)\) | \(\frac{I_mC_m}{2q_\text{max}\Delta \omega}\sin(\Delta\omega t)\) | \(\frac{I_mC_m}{2q_\text{max}\Delta \omega}\sin(\Delta\omega t)\) |
| \(P_{SBC}(\Delta \omega)\) | \(10\log(\frac{I_0^2C_0^2}{16q_\text{max}^2\Delta \omega^2})\) | \(10\log(\frac{I_m^2C_m^2}{16q_\text{max}^2\Delta \omega^2})\) | \(10\log(\frac{I_m^2C_m^2}{16q_\text{max}^2\Delta \omega^2})\) |
\[\begin{align} \mathcal{L}\{\Delta \omega\} &= 10\log\left(\frac{I_0^2C_0^2}{16q_\text{max}^2\Delta \omega^2} + 2\frac{I_m^2C_m^2}{16q_\text{max}^2\Delta \omega^2}\right) \\ &= 10\log\left(\frac{\overline{i_n^2/\Delta f}\cdot \frac{C_0^2}{2} }{4q_\text{max}^2\Delta \omega^2} + \frac{\overline{i_n^2/\Delta f}\cdot\sum_{m=1}^\infty C_m^2 }{4q_\text{max}^2\Delta \omega^2}\right) \\ &= 10\log \frac{\overline{i_n^2/\Delta f}(C_0^2/2+\sum_{m=1}^\infty C_m^2)}{4q_\text{max}^2\Delta \omega^2} \\ &= 10\log \frac{\overline{i_n^2/\Delta f}\cdot \Gamma_\text{rms}^2}{2q_\text{max}^2\Delta \omega^2} \end{align}\]
ISF & \(1/f\)-noise up-conversion
TODO 📅
ISF Simulation

PSS + PXF Method
Yizhe Hu, "A Simulation Technique of Impulse Sensitivity Function (ISF) Based on Periodic Transfer Function (PXF)" [https://bbs.eetop.cn/thread-869343-1-1.html]
TODO 📅
Transient Method
David Dolt. ECEN 620 Network Theory - Broadband Circuit Design: "VCO ISF Simulation" [https://people.engr.tamu.edu/spalermo/ecen620/ISF_SIM.pdf]
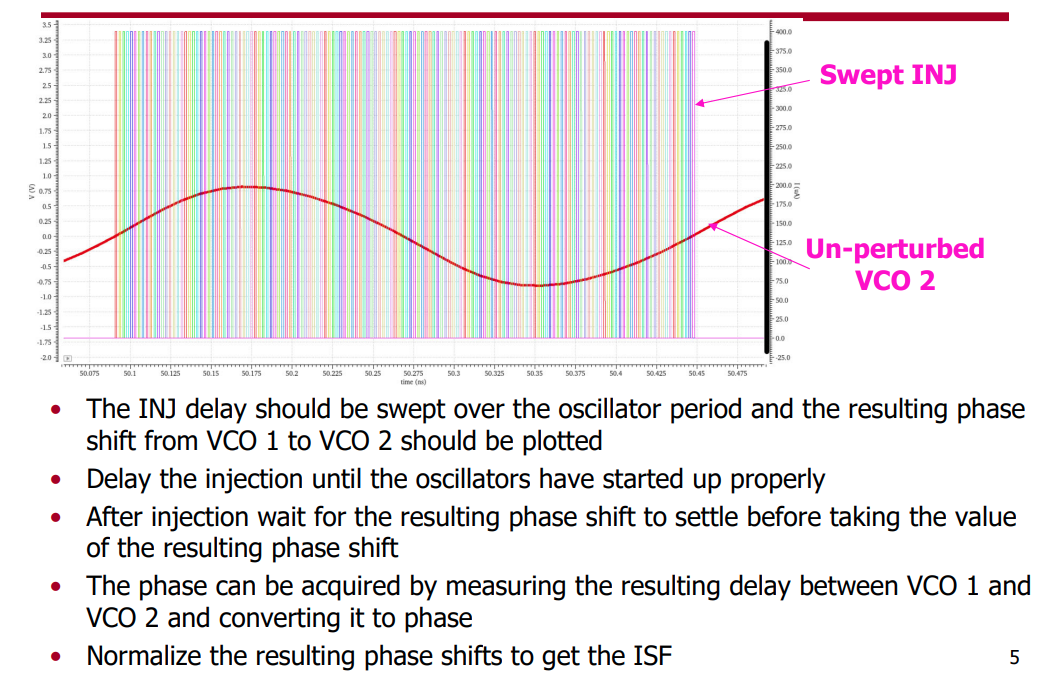
To compare the ring oscillator and VCO the total injected charge to both should be the same
Demir's Model - NLTV PPV

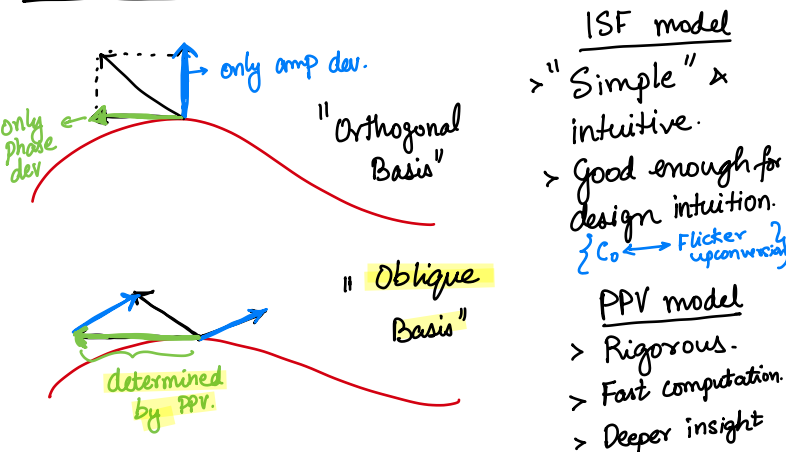
PPV (Perturbation Projection Vector)
A. Demir and J. Roychowdhury, "A reliable and efficient procedure for oscillator PPV computation, with phase noise macromodeling applications," in IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems, vol. 22, no. 2, pp. 188-197, Feb. 2003 [https://sci-hub.se/10.1109/TCAD.2002.806599]
Helene Thibieroz, Customer Support CIC. Using Spectre RF Noise-Aware PLL Methodology to Predict PLL Behavior Accurately [https://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/document?repid=rep1&type=pdf&doi=3056e59ea76165373f90152f915a829d25dabebc]
Aditya Varma Muppala. Perturbation Projection Vector (PPV) Theory | Oscillators 11 | MMIC 16 [youtu.be, notes]
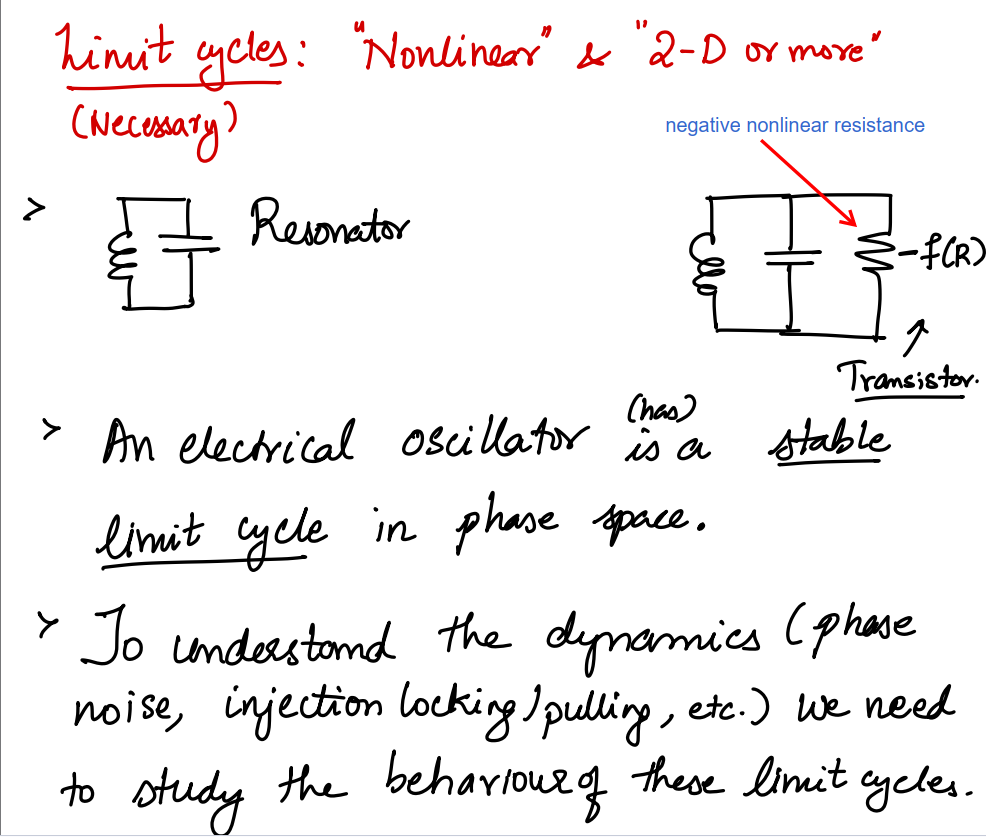
Limit Cycles
[https://adityamuppala.github.io/assets/Notes_YouTube/MMIC_Limit_Cycles.pdf]
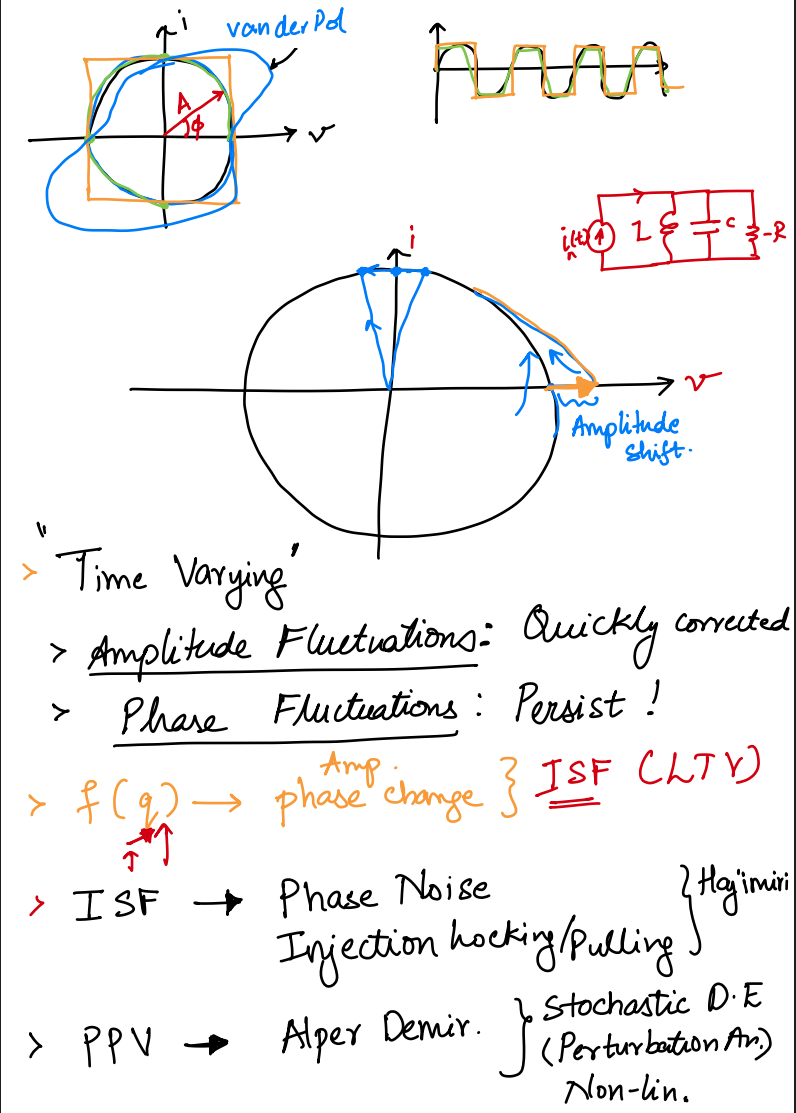
Nonlinear Dynamics
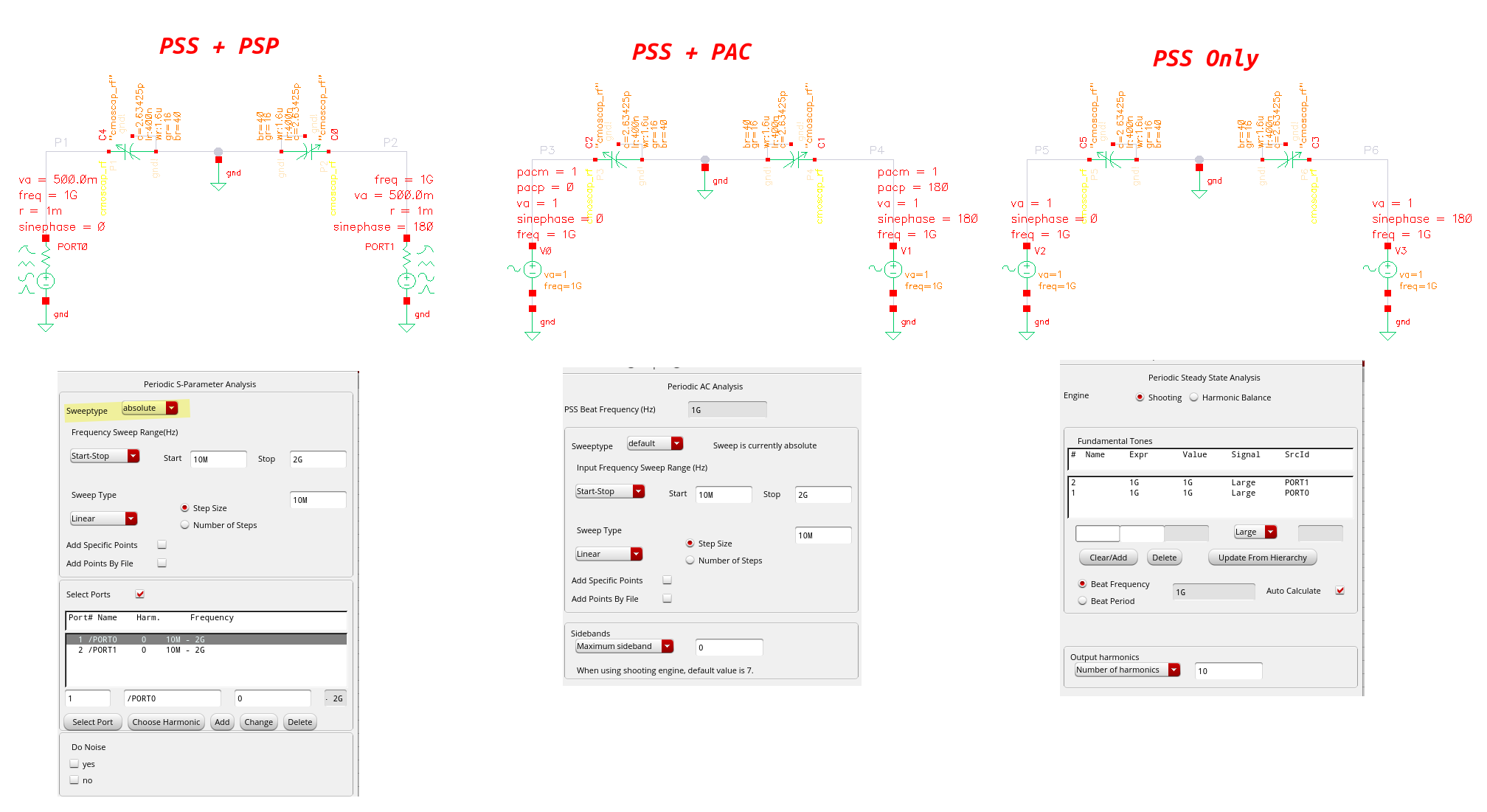
varactor simulation
Three methods:
- PSS +PSP (pay attention to port termination and voltage amplitude)
- PSS +PAC
- PSS Only
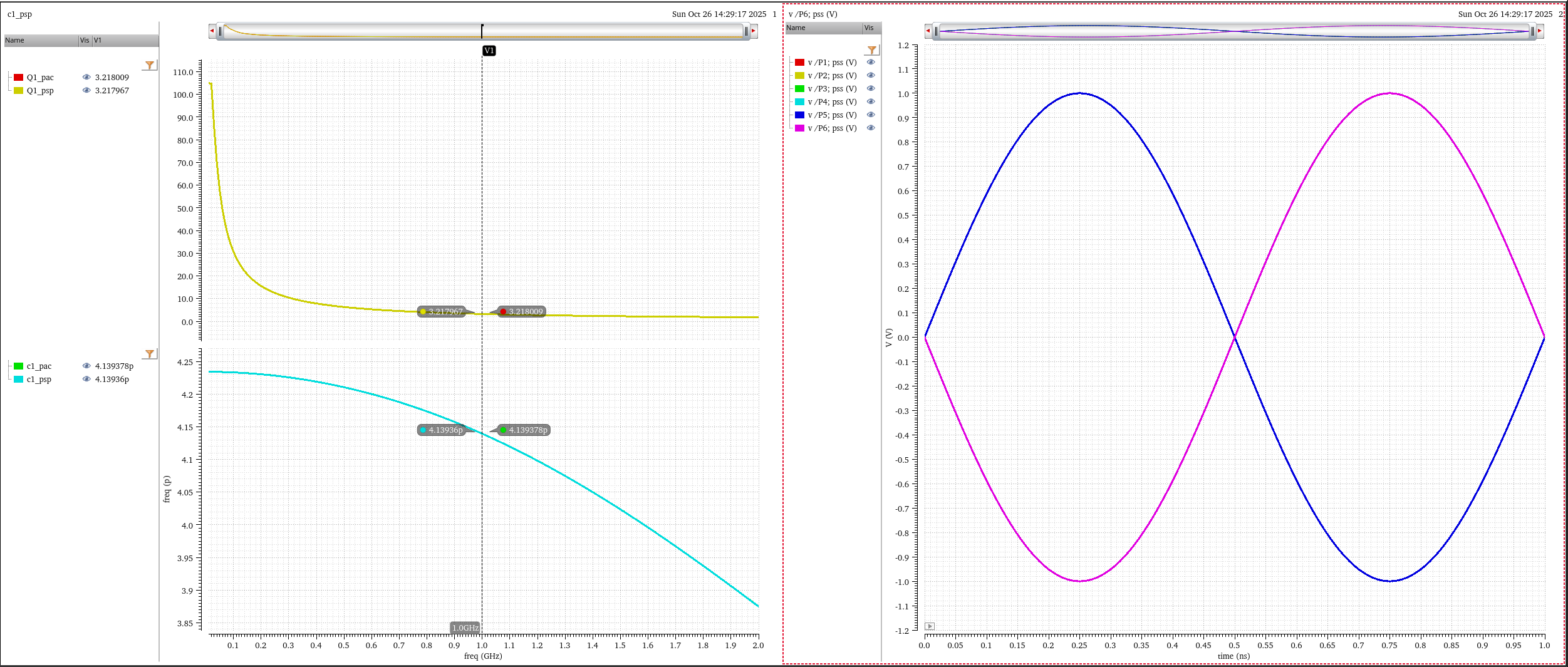
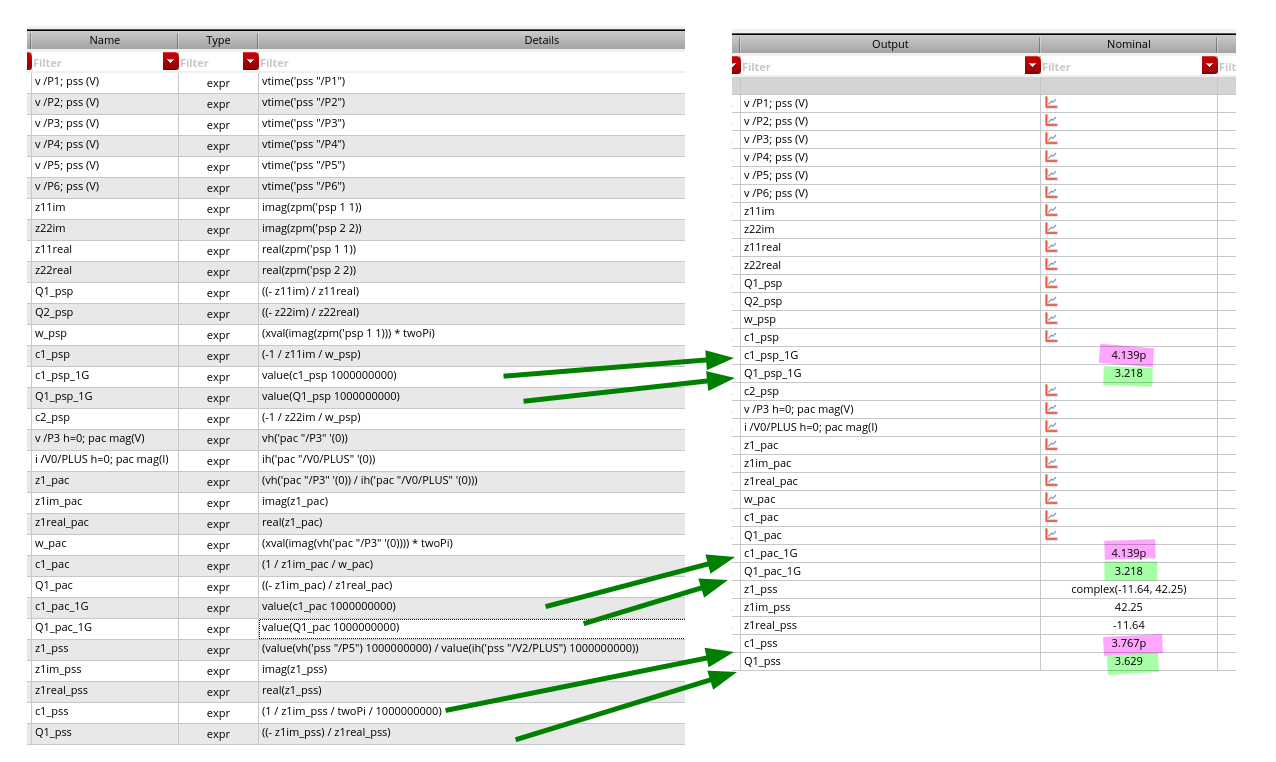
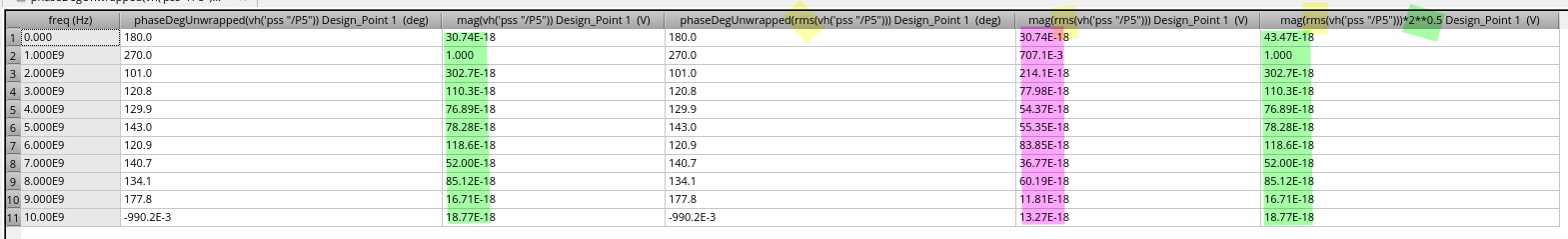
rms only scale magnitude \(1/\sqrt{2}\) but retain phase for complex
number, like harmonic
mag(vh('pss "/P5"))=mag(rms(vh('pss "/P5"))) * (2**0.5)phaseDegUnwrapped(vh('pss "/P5"))=phaseDegUnwrapped(rms(vh('pss "/P5")))
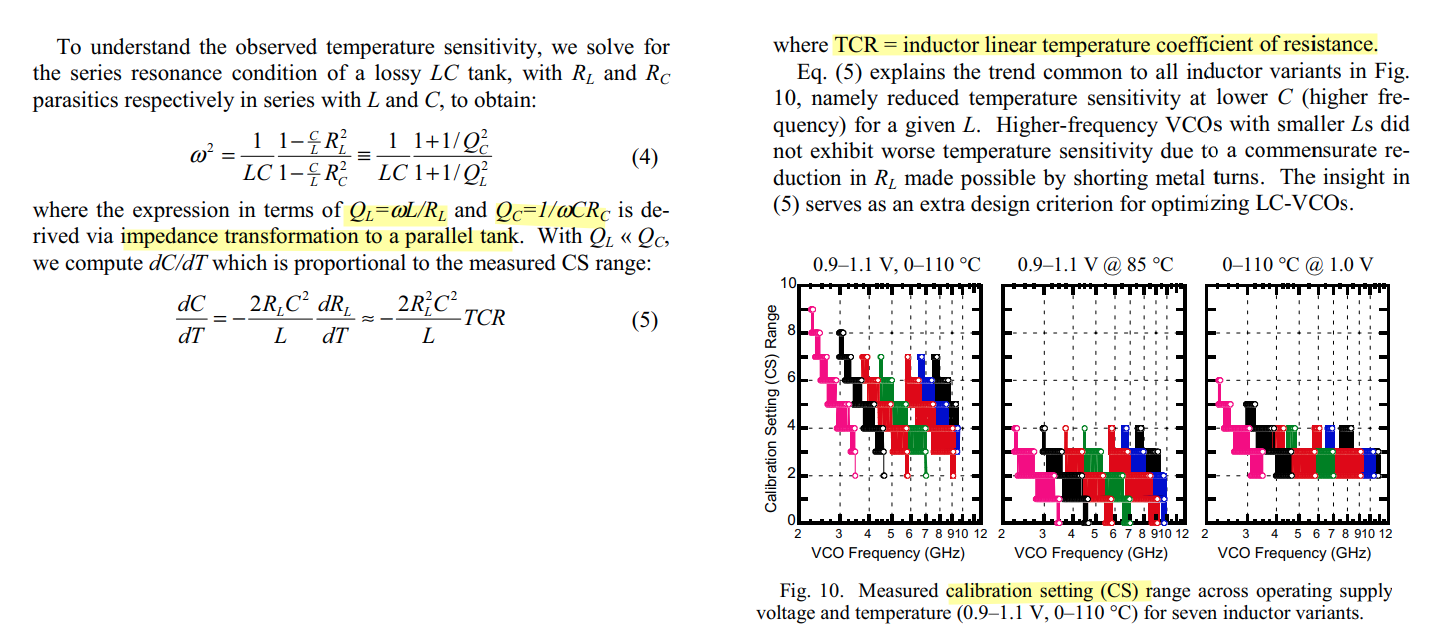
LC-VCO Temperature Sensitivities
A. L. S. Loke et al., "A versatile low-jitter PLL in 90-nm CMOS for SerDes transmitter clocking," Proceedings of the IEEE 2005 Custom Integrated Circuits Conference, 2005., San Jose, CA, USA, 2005 [slides, paper]
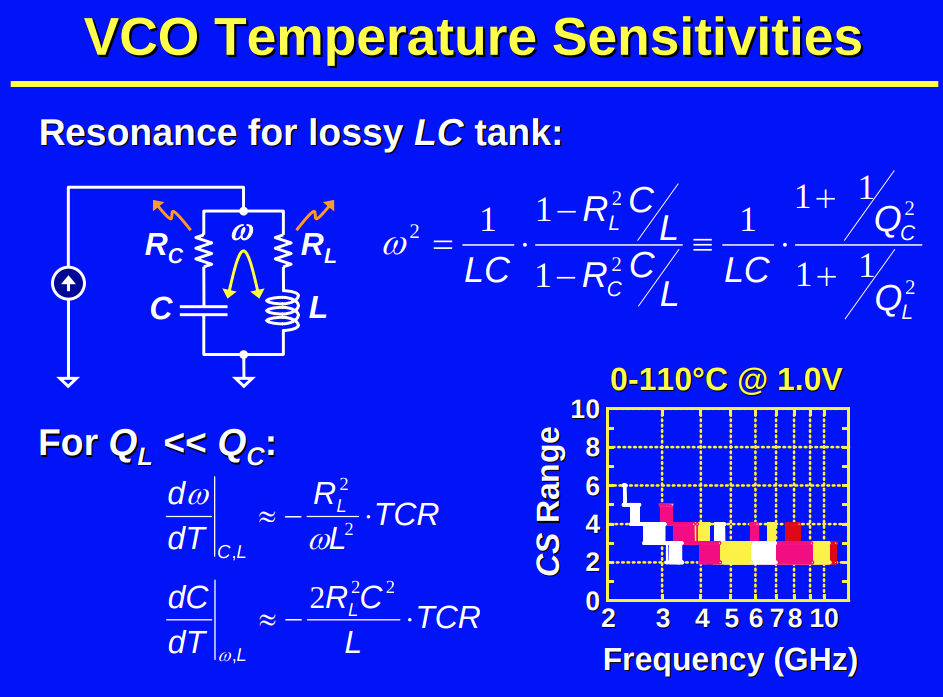
\[ f=\frac{1}{2\pi\sqrt{L_p C_p}} = \frac{1}{2\pi\sqrt{L_s\frac{Q_L^2+1}{Q_L^2} C_s\frac{Q_C^2}{Q_C^2+1}}} = \frac{1}{2\pi\sqrt{L_sC_s}}\cdot \sqrt{\frac{1+1/Q_c^2}{1+1/Q_L^2}} \] Assuming the tank's Q is limited by the inductor's quality factor \(Q_L\), i.e. \(Q_L\ll Q_c\) \[ f\approx \frac{1}{2\pi\sqrt{L_sC_s}}\cdot \sqrt{1-\frac{1}{Q_L^2}} =f_0\cdot\sqrt{1-\frac{1}{Q_L^2}} \] where \(f_0=\frac{1}{\sqrt{L_sC_s}}\) is the first order approximation of the resonant frequency
reference
Jiří Lebl. Notes on Diffy Qs: Differential Equations for Engineers [link]
Matt Charnley. Differential Equations: An Introduction for Engineers [link]
Åström, K.J. & Murray, Richard. (2021). Feedback Systems: An Introduction for Scientists and Engineers Second Edition [https://www.cds.caltech.edu/~murray/books/AM08/pdf/fbs-public_24Jul2020.pdf]
Strogatz, S.H. (2015). Nonlinear Dynamics and Chaos: With Applications to Physics, Biology, Chemistry, and Engineering (2nd ed.). CRC Press [https://www.biodyn.ro/course/literatura/Nonlinear_Dynamics_and_Chaos_2018_Steven_H._Strogatz.pdf]
Cadence Blog, "Resonant Frequency vs. Natural Frequency in Oscillator Circuits" [link]
Aditya Varma Muppala. Oscillators [https://youtube.com/playlist?list=PL9Trid0A4Da2fOmYTEjhAnUkGPxyiH7H6&si=ILxn8hfkMYjXW5f4]
P.E. Allen - 2003. ECE 6440 - Frequency Synthesizers: Lecture 160 – Phase Noise - II [https://pallen.ece.gatech.edu/Academic/ECE_6440/Summer_2003/L160-PhNoII(2UP).pdf]
Y. Hu, T. Siriburanon and R. B. Staszewski, "Intuitive Understanding of Flicker Noise Reduction via Narrowing of Conduction Angle in Voltage-Biased Oscillators," in IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, vol. 66, no. 12, pp. 1962-1966, Dec. 2019 [https://sci-hub.se/10.1109/TCSII.2019.2896483]
S. Levantino, P. Maffezzoni, F. Pepe, A. Bonfanti, C. Samori and A. L. Lacaita, "Efficient Calculation of the Impulse Sensitivity Function in Oscillators," in IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, vol. 59, no. 10, pp. 628-632, Oct. 2012 [https://sci-hub.se/10.1109/TCSII.2012.2208679]
S. Levantino and P. Maffezzoni, "Computing the Perturbation Projection Vector of Oscillators via Frequency Domain Analysis," in IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems, vol. 31, no. 10, pp. 1499-1507, Oct. 2012 [https://sci-hub.se/10.1109/TCAD.2012.2194493]
Thomas H. Lee. Linearity, Time-Variation, Phase Modulation and Oscillator Phase Noise [https://class.ece.iastate.edu/djchen/ee507/PhaseNoiseTutorialLee.pdf]
Y. Hu, T. Siriburanon and R. B. Staszewski, "Oscillator Flicker Phase Noise: A Tutorial," in IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, vol. 68, no. 2, pp. 538-544, Feb. 2021 [https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=9286468]
Jaeha Kim. Lecture 8. Special Topics: Design Trade -Offs in LC -Tuned Oscillators [https://ocw.snu.ac.kr/sites/default/files/NOTE/7033.pdf]
A. Demir, A. Mehrotra and J. Roychowdhury, "Phase noise in oscillators: a unifying theory and numerical methods for characterization," in IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Fundamental Theory and Applications, vol. 47, no. 5, pp. 655-674, May 2000 [https://sci-hub.se/10.1109/81.847872]
A. A. Abidi and D. Murphy, "How to Design a Differential CMOS LC Oscillator," in IEEE Open Journal of the Solid-State Circuits Society, vol. 5, pp. 45-59, 2025 [https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?arnumber=10818782]
Akihide Sai, Toshiba. ISSCC 2023 T5: All-digital PLLs From Fundamental Concepts to Future Trends [https://www.nishanchettri.com/isscc-slides/2023%20ISSCC/TUTORIALS/T5.pdf]
Pietro Andreani. ISSCC 2011 T1: Integrated LC oscillators [slides,transcript]
—. ISSCC 2017 F2: Integrated Harmonic Oscillators
—. SSCS Distinguished Lecture: RF Harmonic Oscillators Integrated in Silicon Technologies [https://www.ieeetoronto.ca/wp-content/uploads/2020/06/DL-Toronto.pdf]
—. ESSCIRC 2019 Tutorials: RF Harmonic Oscillators Integrated in Silicon Technologies [https://youtu.be/k1I9nP9eEHE?si=fns9mf3aHjMJobPH]
—. "Harmonic Oscillators in CMOS—A Tutorial Overview," in IEEE Open Journal of the Solid-State Circuits Society, vol. 1, pp. 2-17, 2021 [pdf]
C. Samori, "Tutorial: Understanding Phase Noise in LC VCOs," 2016 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference (ISSCC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 2016
—, "Understanding Phase Noise in LC VCOs: A Key Problem in RF Integrated Circuits," in IEEE Solid-State Circuits Magazine, vol. 8, no. 4, pp. 81-91, Fall 2016 [https://sci-hub.se/10.1109/MSSC.2016.2573979]
—, Phase Noise in LC Oscillators: From Basic Concepts to Advanced Topologies [https://www.ieeetoronto.ca/wp-content/uploads/2020/06/DL-VCO-short.pdf]
Jun Yin. ISSCC 2025 T10: mm-Wave Oscillator Design
Hegazi, Emad, Asad Abidi, and Jacob Rael. The Designer's Guide to High-purity Oscillators. [New York]: Kluwer Academic Publishers, 2005. The Designer's Guide to High-Purity Oscillators [pdf]