Digital Phase-Locked Loops
Hunting Jitter
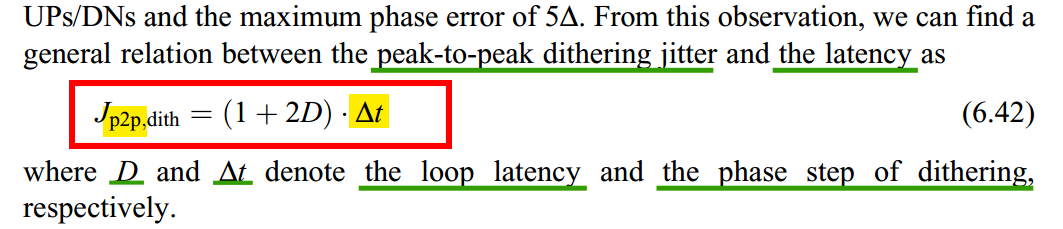
Hunting jitter is often referred to as dithering jitter, the periodic time error between data clock and input data, which exhibits a limit-cycle behavior

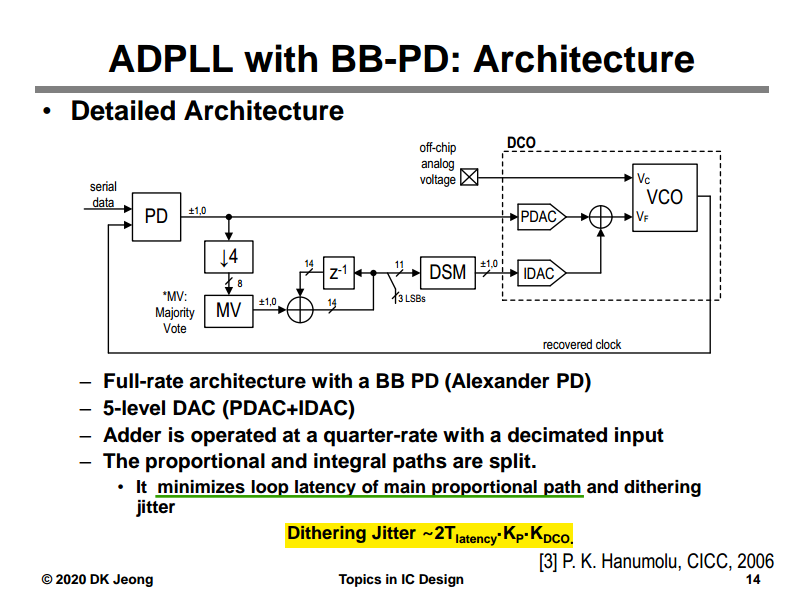
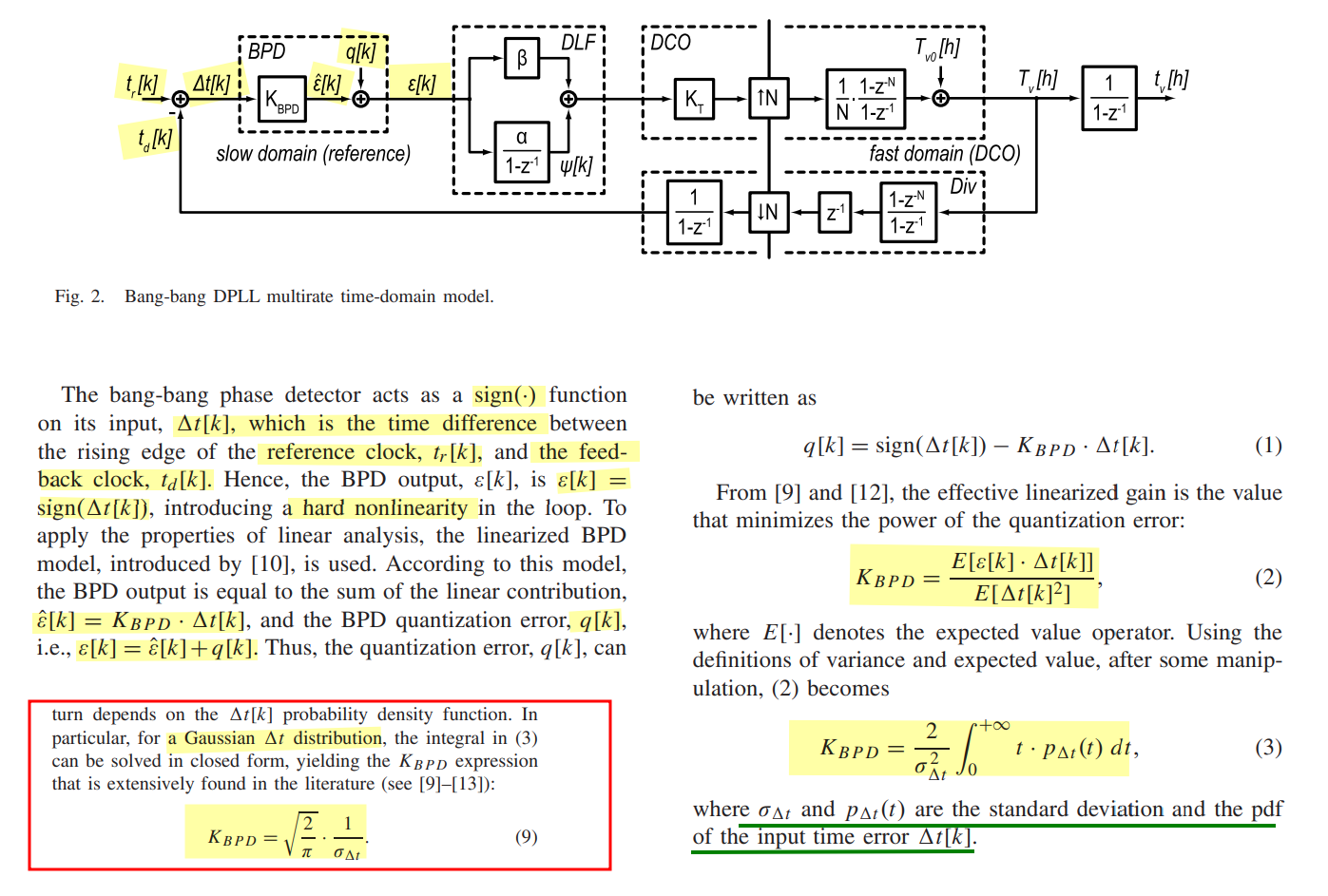
BB PD
Youngdon Choi, Deog-Kyoon Jeong and W. Kim, "Jitter transfer analysis of tracked oversampling techniques for multigigabit clock and data recovery," in IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Analog and Digital Signal Processing, vol. 50, no. 11, pp. 775-783, Nov. 2003 [https://sci-hub.st/10.1109/TCSII.2003.819070]
John T. Stonick, ISSCC 2011 TUTORIALS T5: DPLL-Based Clock and Data Recovery [slides transcript]
Walker, Richard. (2003). Designing Bang-Bang PLLs for Clock and Data Recovery in Serial Data Transmission Systems. [pdf]
—, Clock and Data Recovery for Serial Data Communications, focusing on bang-bang CDR design methodology, ISSCC Short Course, February 2002. [slides]
It's ternary, because early, late and no transition
notice the transition density = 1 in digital PLL
Linearization
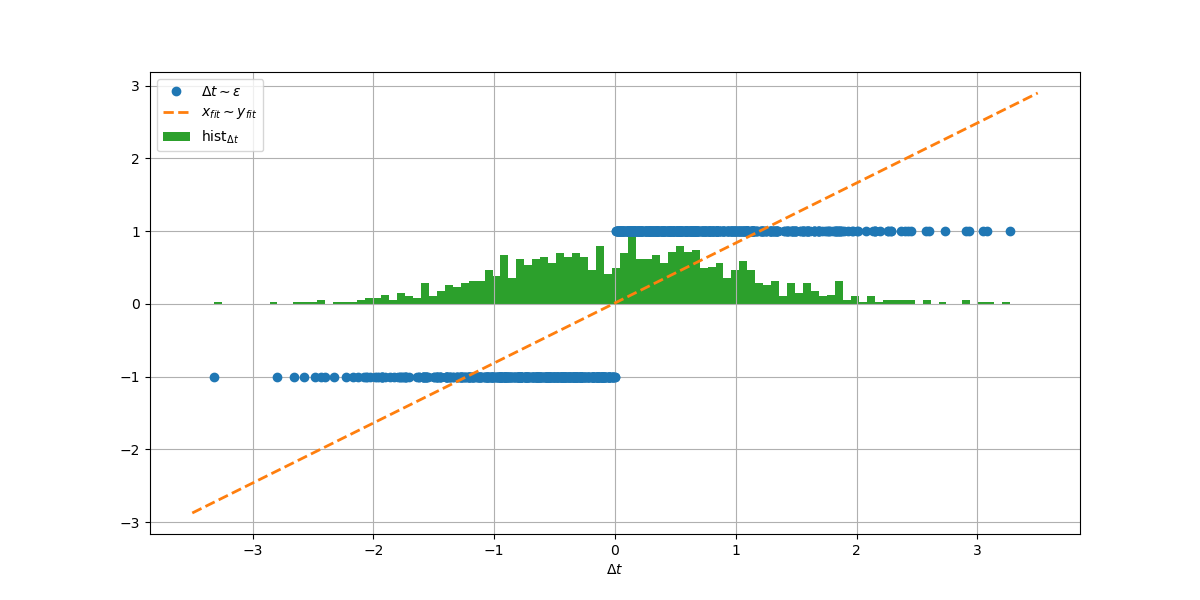
The effective PD gain is a function of the input jitter pdf, it enables one to anticipate the effects of input jitter on loop characteristics
BB Gain is the slope of average BB output \(\mu\), versus phase offset \(\phi\), i.e. \(\frac {\partial \mu}{\partial \phi}\),
BB only produces output for a transition and this de-rates the gain. Transition density = 0.5 for random data
\[ K_{BB} = \frac{1}{2}\frac {\partial \mu}{\partial \phi} \]
where \(\mu = (1)\times \mathrm{P}(\text{late}|\phi) + (-1)\times \mathrm{P}(\text{early}|\phi)\)
Both jitter and amplitude noise distribution are same, just scaled by slope
Self-Noise Term
One price we pay for BB PD versus linear PD is the self-noise term. For small phase errors BB output noise is the full magnitude of the sliced data
The PD output should be almost 0 for small phase errors. i.e. ideal PD output noise should be 0
\[ \sigma_{BB}^2 = 1^2 \cdot \mathrm{P}(\text{trans}) + 0^2\cdot (1-\mathrm{P}(\text{trans})) = 0.5 \]
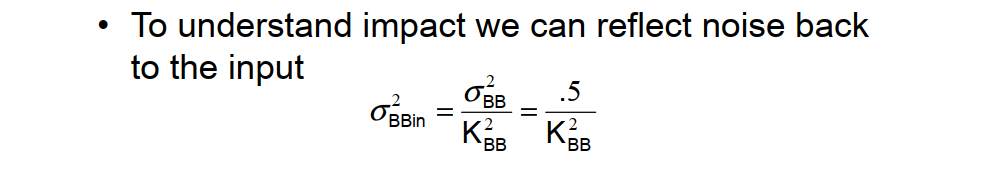
Input referred jitter from BB PD is proportional to incoming jitter
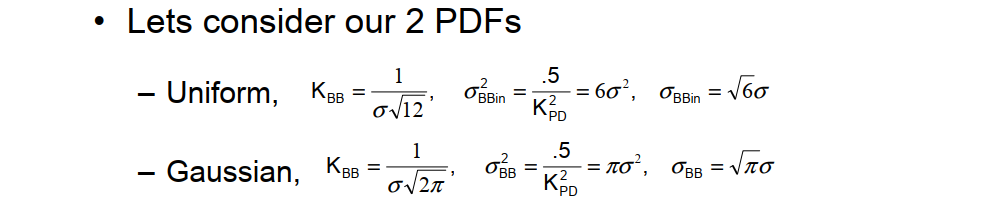
gain simulation
L. Avallone, M. Mercandelli, A. Santiccioli, M. P. Kennedy, S. Levantino and C. Samori, "A Comprehensive Phase Noise Analysis of Bang-Bang Digital PLLs," in IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, vol. 68, no. 7, pp. 2775-2786, July 2021 [https://sci-hub.st/10.1109/TCSI.2021.3072344]
T. -K. Kuan and S. -I. Liu, "A Bang Bang Phase-Locked Loop Using Automatic Loop Gain Control and Loop Latency Reduction Techniques," in IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, vol. 51, no. 4, pp. 821-831, April 2016 [https://sci-hub.st/10.1109/JSSC.2016.2519391]
1 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt |
Pavan, Shanthi, Richard Schreier, and Gabor Temes. (2016). Understanding Delta-Sigma Data Converters. 2nd ed. Wiley. - 2.2.1 Quantizer Modeling
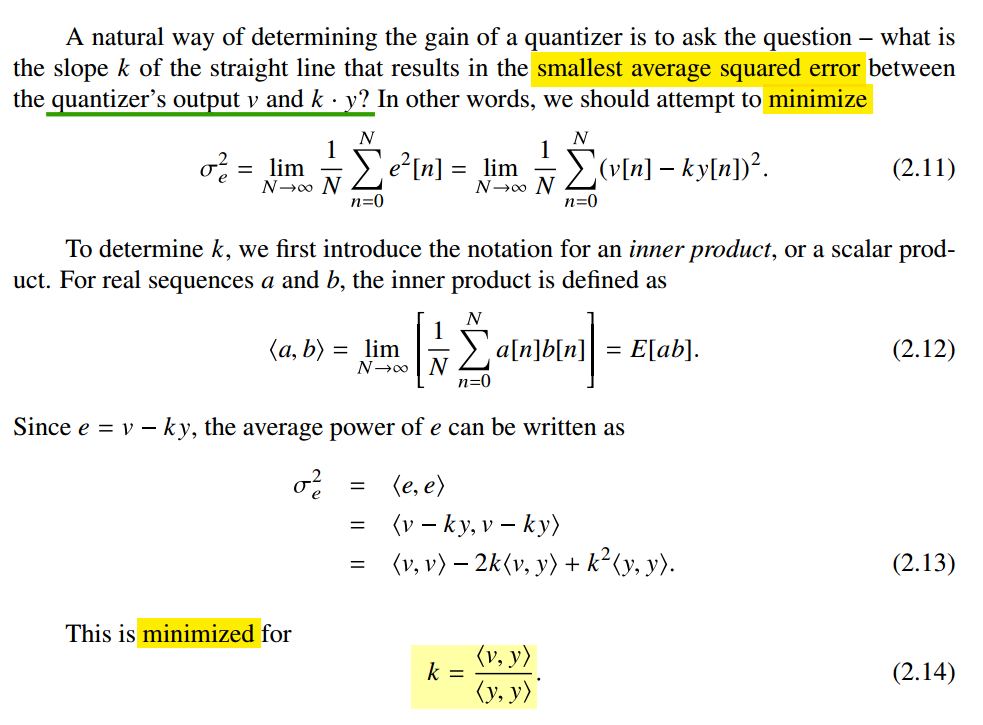 \[
\frac{d\sigma_e^2}{dk} =0\space\space\Rightarrow\space\space
k=\frac{\left\langle v,y\right\rangle}{\left\langle y,y \right\rangle}
\]
\[
\frac{d\sigma_e^2}{dk} =0\space\space\Rightarrow\space\space
k=\frac{\left\langle v,y\right\rangle}{\left\langle y,y \right\rangle}
\]
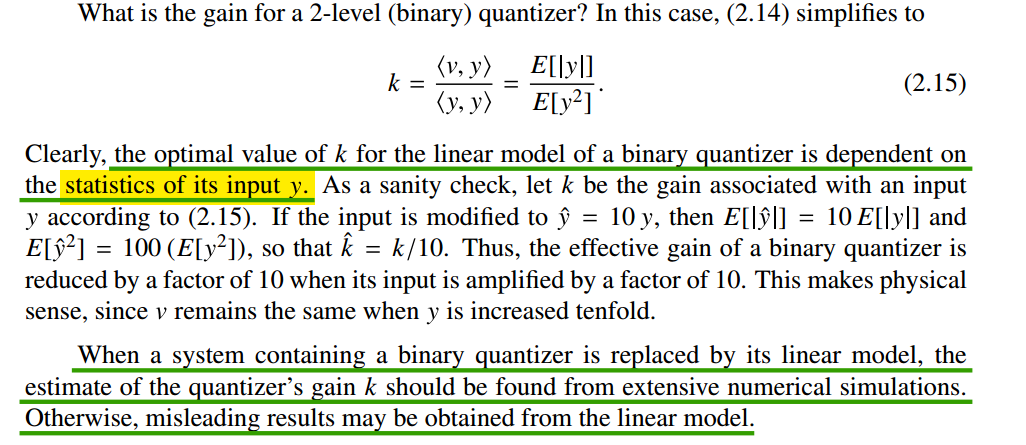
DCO Quantization Noise
TODO 📅
TDC Quantization Noise
TODO 📅
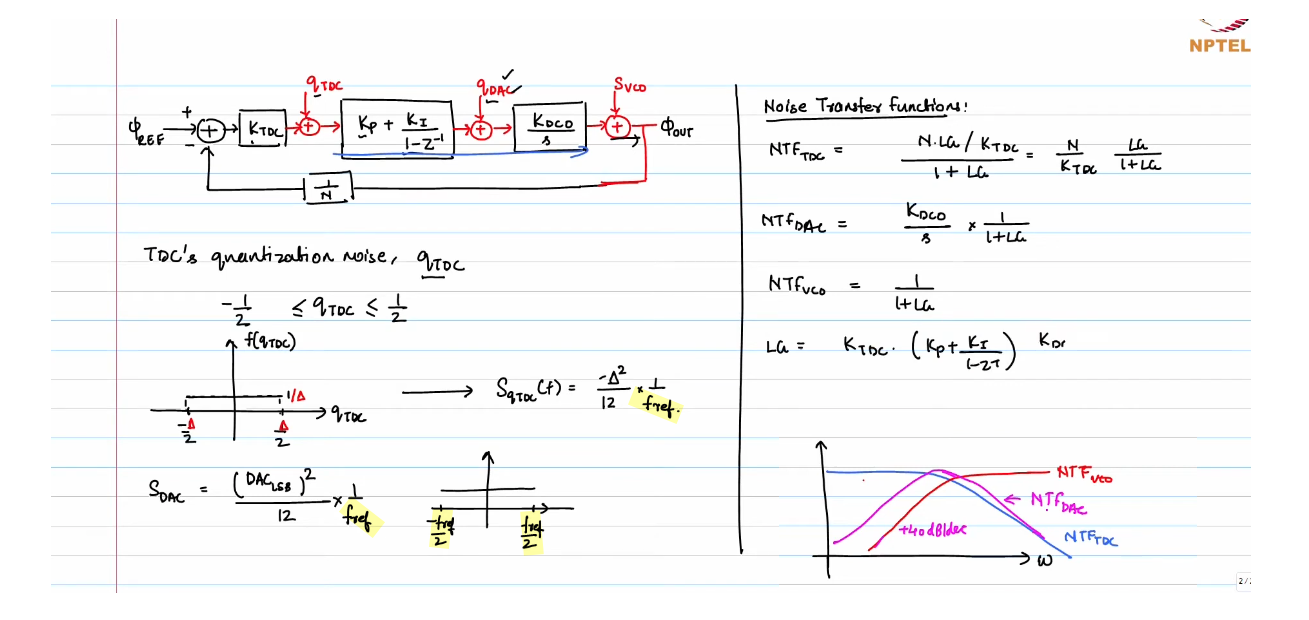
CDR Loop Latency
Amir Amirkhany. ISSCC 2019 "Basics of Clock and Data Recovery Circuits"
CC Chen. Why A Low Loop Latency in A CDR Design? [https://youtu.be/io9WZbhlahU]
—. Why Understanding and Optimizing Loop Latency for A CDR Design? [https://youtu.be/Jyy18865jv8]
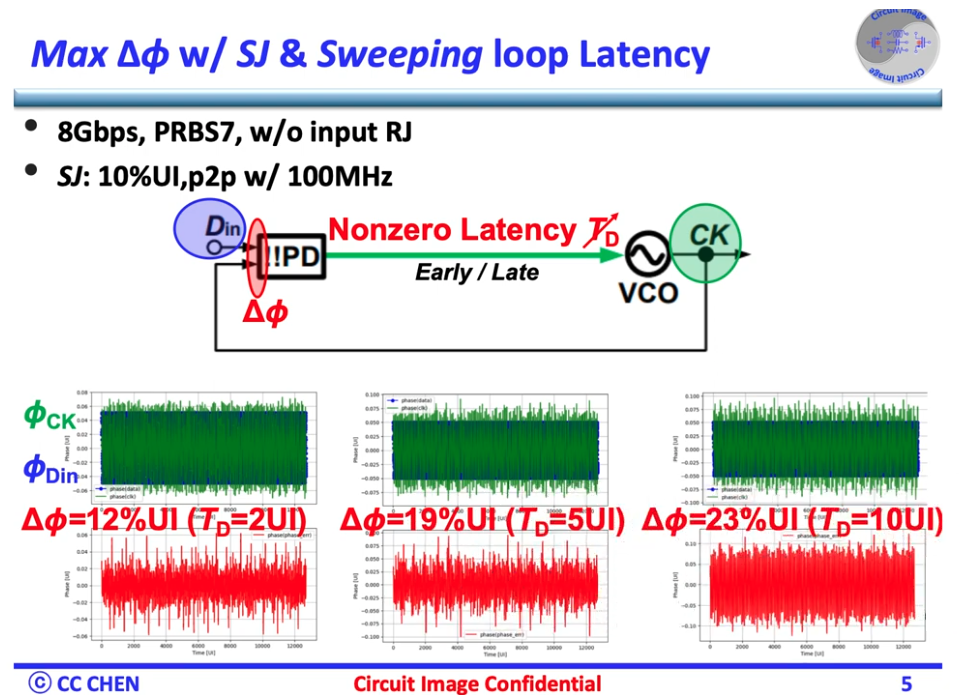
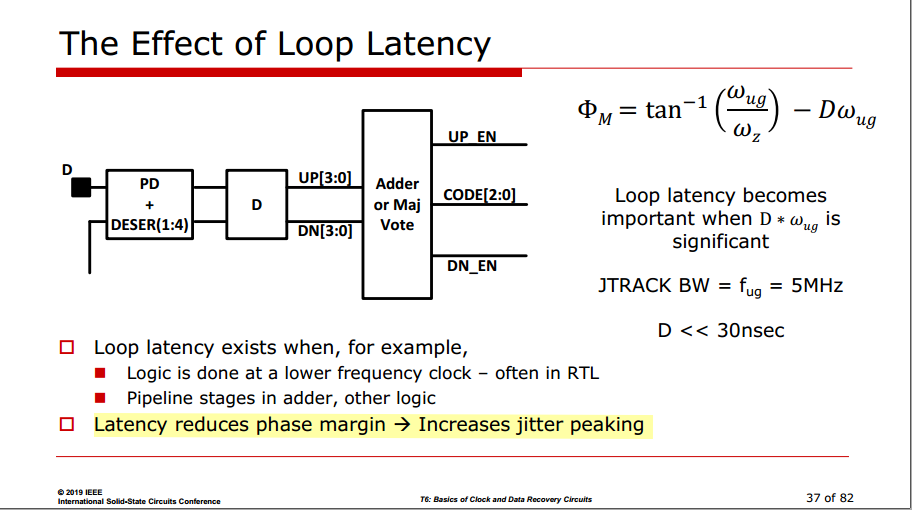
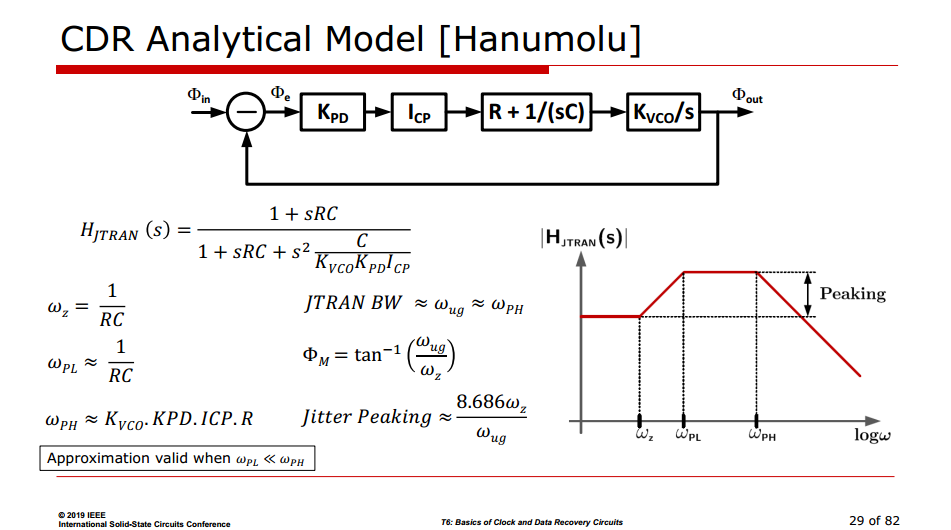
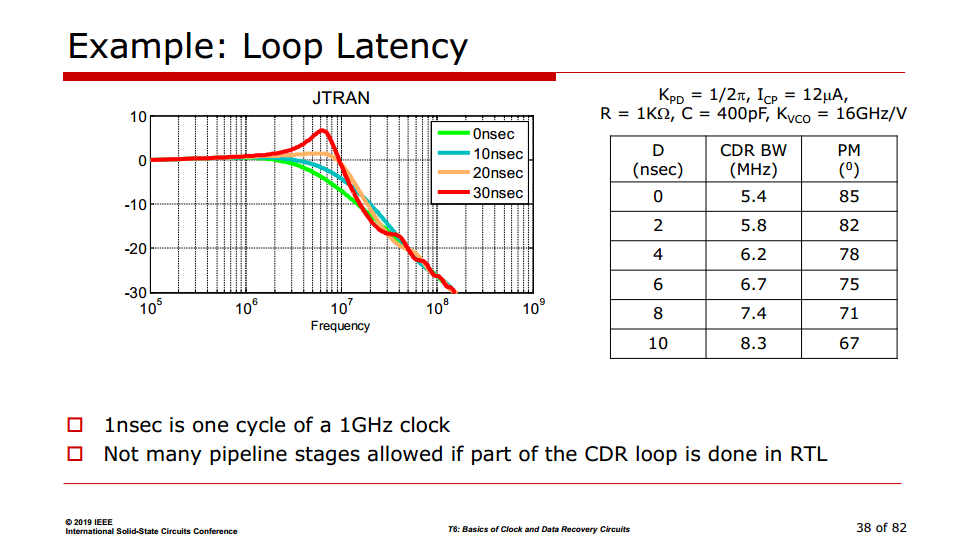
loop latency is represented as \(e^{-sD}\) in linear model
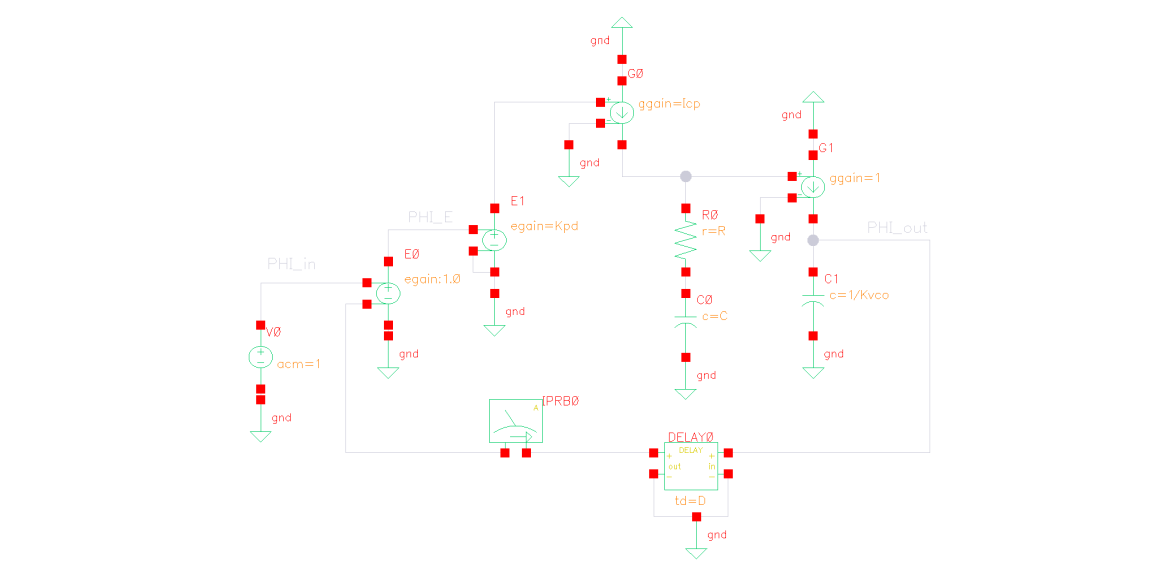
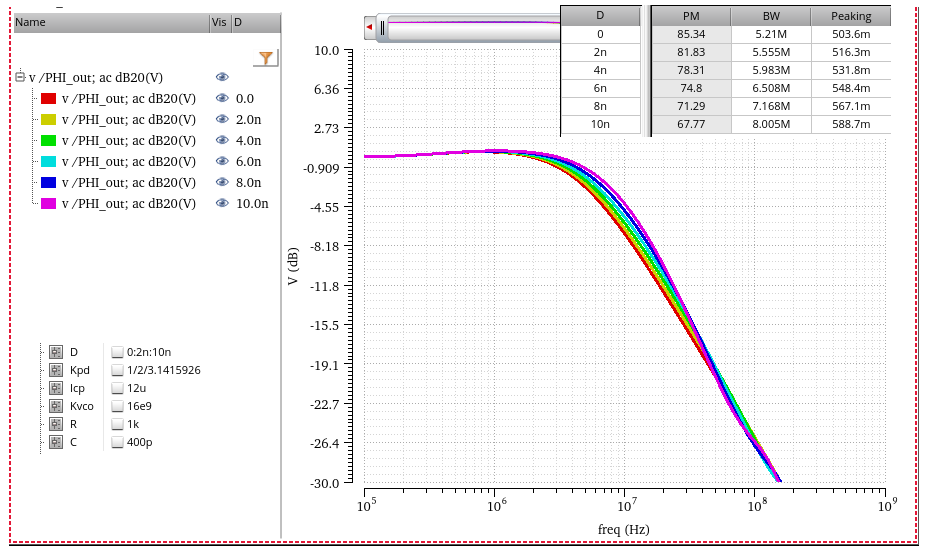
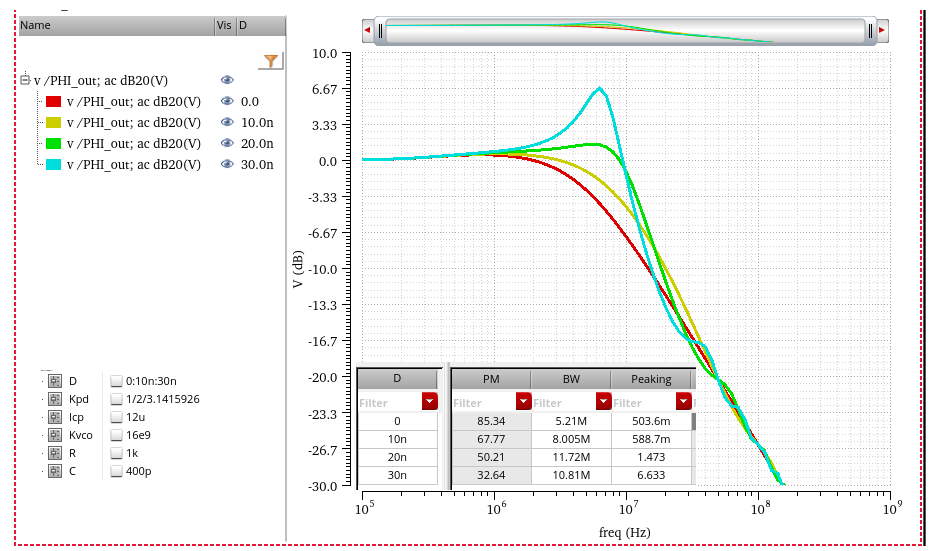
Sensitivity to Loop Latency
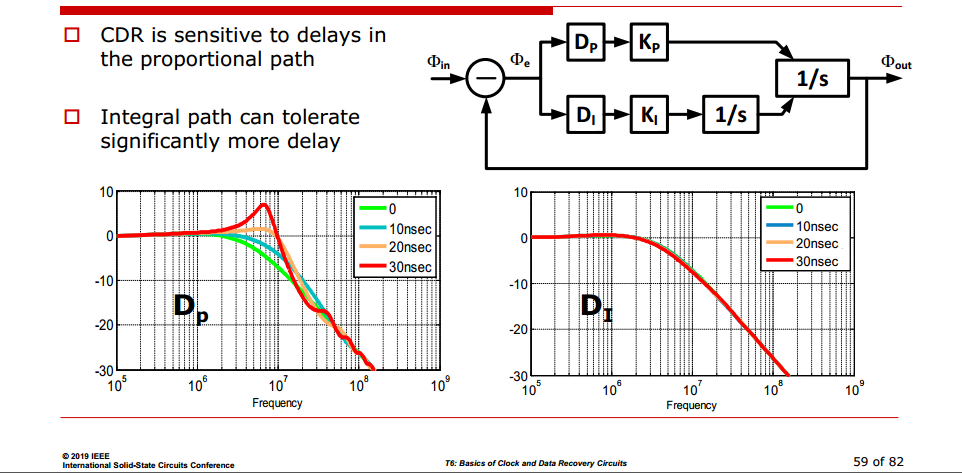
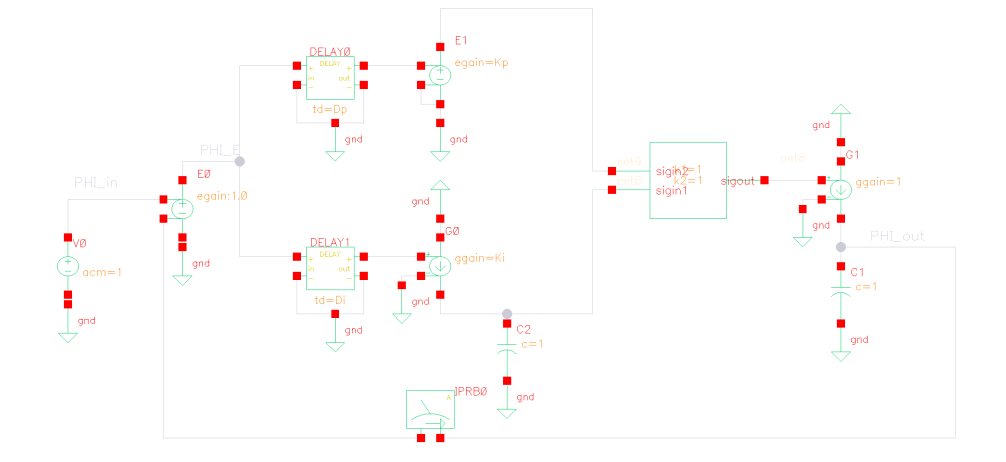
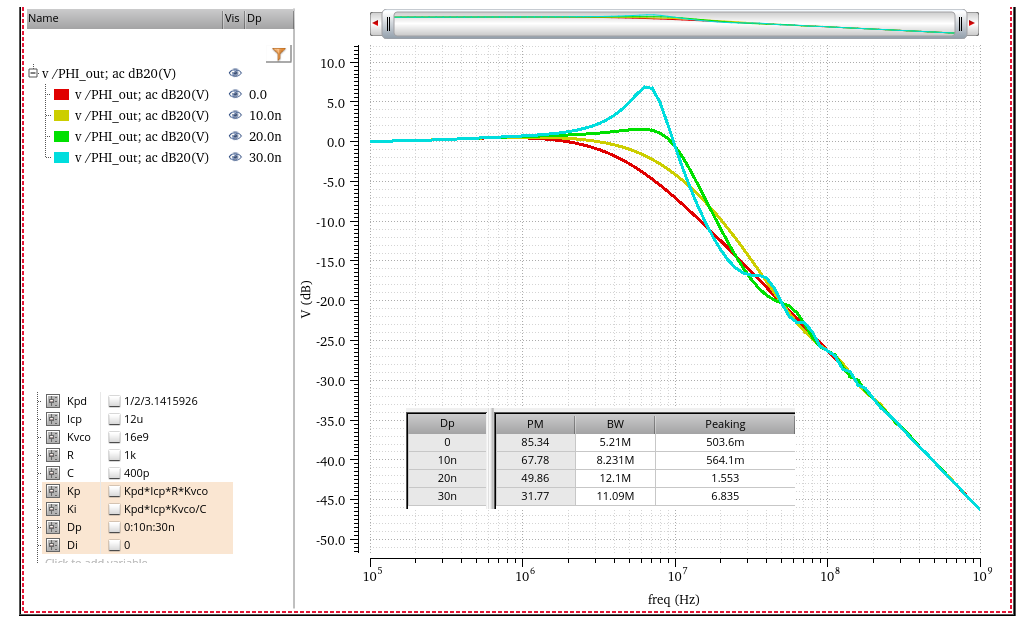
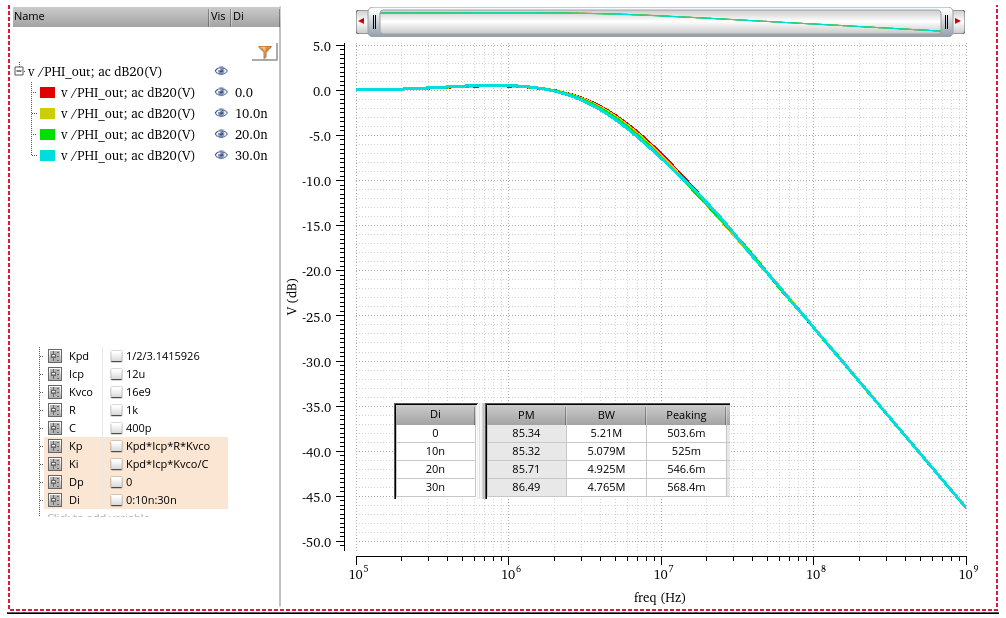
Optimizing Loop Latency
TODO 📅
CC Chen. Circuit Image: Why Understanding and Optimizing Loop Latency for A CDR Design? [https://youtu.be/Jyy18865jv8?si=uY2HUV8mERLterwH]
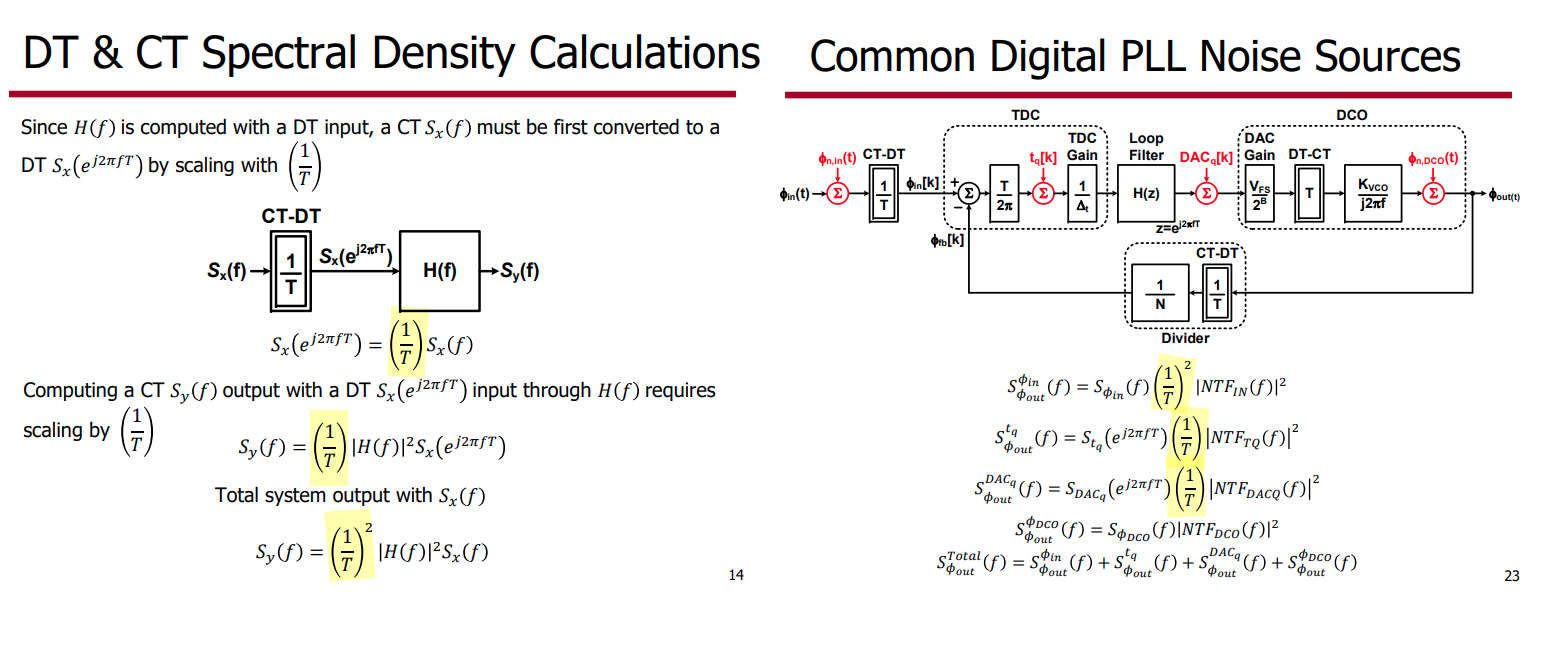
DT & CT Spectral Density
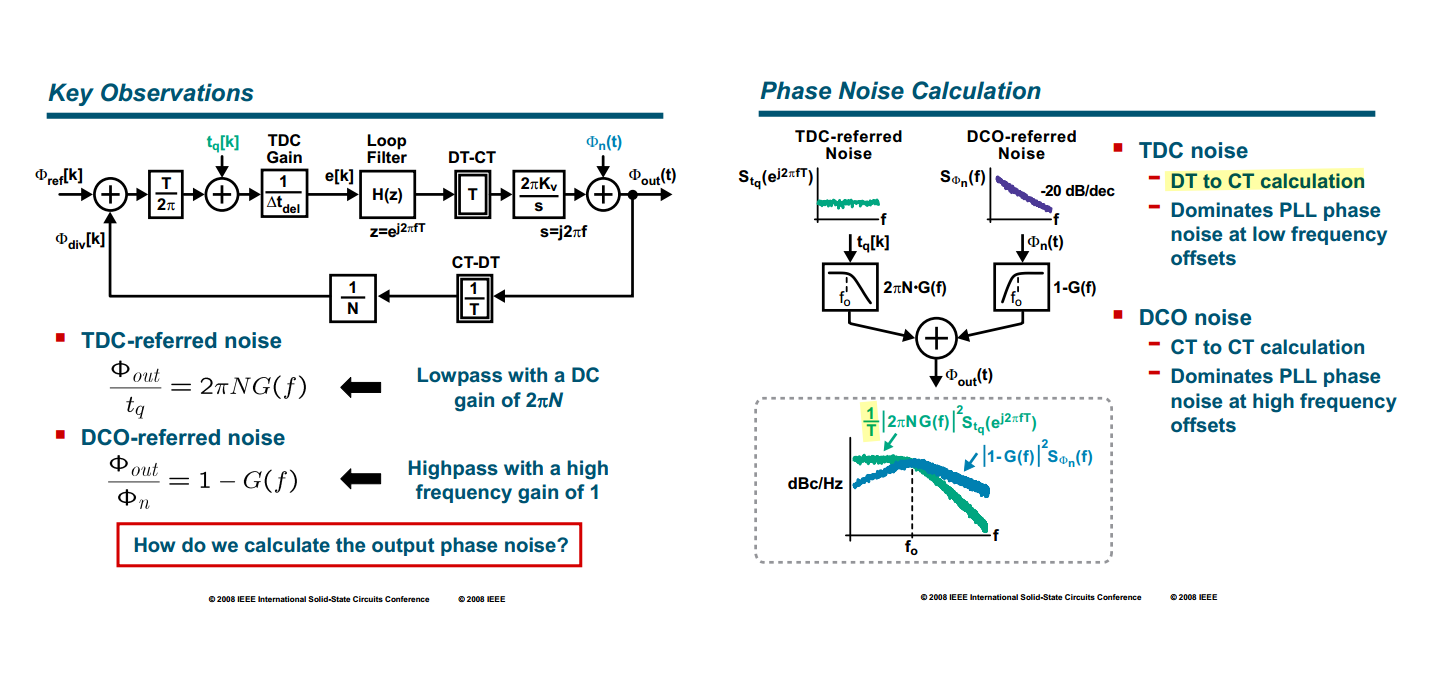
[Sampling of WSS process of Systems, Modulation and Noise]
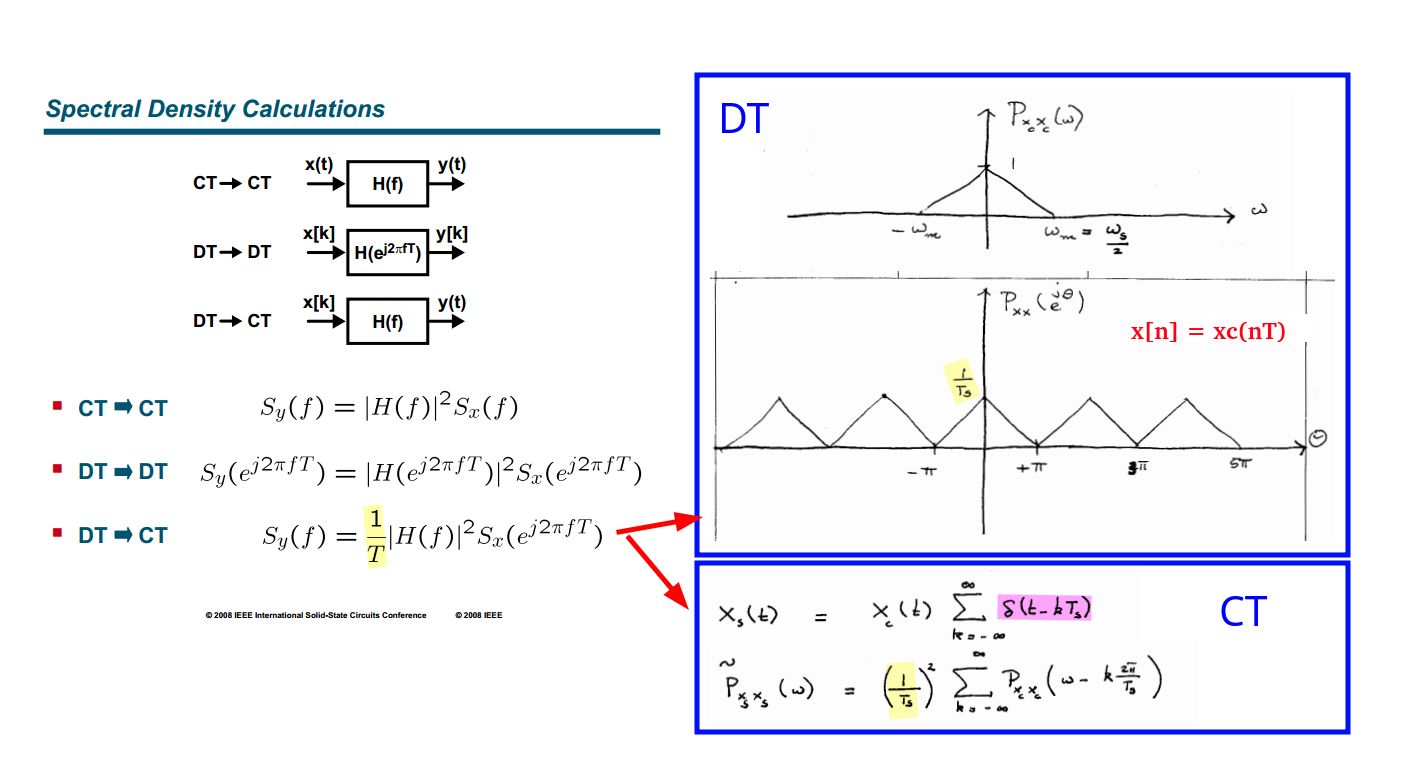
That is \[ P_{x_s x_s} (f)= \frac{1}{T_s}P_{xx}(f) \] In going from discrete time to continuous time, we must add a scale factor \(1/T\), the sample period
reference
Sam Palermo, ECEN620 2024 Lecture 9: Digital PLLs [https://people.engr.tamu.edu/spalermo/ecen620/lecture09_ee620_digital_PLLs.pdf]
Topics in IC(Wireline Transceiver Design) [https://ocw.snu.ac.kr/sites/default/files/NOTE/Lec%203%20-%20ADPLL.pdf]
Michael H. Perrott, ISSCC 2008 Tutorial on Digital Phase-Locked Loops [https://www.nishanchettri.com/isscc-slides/2008%20ISSCC/Tutorials/T05_Pres.pdf]
—, CICC 2009 Tutorial on Digital Phase-Locked Loops [https://www.cppsim.com/PLL_Lectures/digital_pll_cicc_tutorial_perrott.pdf]
Robert Bogdan Staszewski, CICC 2020: Beyond All-Digital PLL for RF and Millimeter-Wave Frequency Synthesis [link]
Akihide Sai, ISSCC 2023 T5: All-digital PLLs From Fundamental Concepts to Future Trends [https://www.nishanchettri.com/isscc-slides/2023%20ISSCC/TUTORIALS/T5.pdf]
Mike Shuo-Wei Chen, CICC 2020 ES2-3: Low-Spur PLL Architectures and Techniques [https://youtu.be/sgPDchYhN-4?si=FAy8N3SuX6vVpYhl]
S. Levantino, "Digital phase-locked loops," 2018 IEEE Custom Integrated Circuits Conference (CICC), San Diego, CA, USA, 2018 [slides]
Saurabh Saxena, IIT Madras. Phase-Locked Loops: Noise Analysis in Digital PLL [https://youtu.be/mddtxcqfiKU?si=yD15KM9WBkT6c68P]
Y. Hu, T. Siriburanon and R. B. Staszewski, "Multirate Timestamp Modeling for Ultralow-Jitter Frequency Synthesis: A Tutorial," in IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, vol. 69, no. 7, pp. 3030-3036, July 2022
Neil Robertson. Digital PLL's -- Part 1 [https://www.dsprelated.com/showarticle/967.php]
Neil Robertson. Digital PLL's -- Part 2 [https://www.dsprelated.com/showarticle/973.php]
Neil Robertson. Digital PLL's -- Part 3 [https://www.dsprelated.com/showarticle/1177.php]
Daniel Boschen. GRCon24 - Quick Start on Control Loops with Python Workshop [video, slides]
L. Avallone, M. Mercandelli, A. Santiccioli, M. P. Kennedy, S. Levantino and C. Samori, "A Comprehensive Phase Noise Analysis of Bang-Bang Digital PLLs," in IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, vol. 68, no. 7, pp. 2775-2786, July 2021 [https://sci-hub.st/10.1109/TCSI.2021.3072344]
M. Zanuso, D. Tasca, S. Levantino, A. Donadel, C. Samori and A. L. Lacaita, "Noise Analysis and Minimization in Bang-Bang Digital PLLs," in IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, vol. 56, no. 11, pp. 835-839, Nov. 2009 [https://sci-hub.st/10.1109/TCSII.2009.2032470]
N. Da Dalt, "Linearized Analysis of a Digital Bang-Bang PLL and Its Validity Limits Applied to Jitter Transfer and Jitter Generation," in IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, vol. 55, no. 11, pp. 3663-3675, Dec. 2008 [https://sci-hub.st/10.1109/TCSI.2008.925948]
—, "Markov Chains-Based Derivation of the Phase Detector Gain in Bang-Bang PLLs," in IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, vol. 53, no. 11, pp. 1195-1199, Nov. 2006 [https://sci-hub.st/10.1109/TCSII.2006.883197]
—, "A design-oriented study of the nonlinear dynamics of digital bang-bang PLLs," in IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, vol. 52, no. 1, pp. 21-31, Jan. 2005 [https://sci-hub.se/10.1109/TCSI.2004.840089]
—, "Theory and Implementation of Digital Bang-Bang Frequency Synthesizers for High Speed Serial Data Communications", PhD Dissertation, RWTH Aachen University, Aachen, North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany, 2007 [pdf]
Walker, Richard. (2003). Designing Bang-Bang PLLs for Clock and Data Recovery in Serial Data Transmission Systems. [paper,slides]
hunting jitter
S. Jang, S. Kim, S. -H. Chu, G. -S. Jeong, Y. Kim and D. -K. Jeong, "An Optimum Loop Gain Tracking All-Digital PLL Using Autocorrelation of Bang–Bang Phase-Frequency Detection," in IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, vol. 62, no. 9, pp. 836-840, Sept. 2015 [https://sci-hub.st/10.1109/TCSII.2015.2435691] [phd thesis]
Deog-Kyoon Jeong. Topics in IC (Wireline Transceiver Design). Lec 3 - All-Digital PLL [https://ocw.snu.ac.kr/sites/default/files/NOTE/Lec%203%20-%20ADPLL.pdf]
—. Topics in IC (Wireline Transceiver Design). Lec 6 - Clock and Data Recovery [https://ocw.snu.ac.kr/sites/default/files/NOTE/Lec%206%20-%20Clock%20and%20Data%20Recovery.pdf]
Lee Hae-Chang.: ‘An estimation approach to clock and data recovery’, PhD Thesis, Stanford University, November 2006 [pdf]
J. Kim, Design of CMOS Adaptive-Supply Serial Links, Ph.D. Thesis, Stanford University, December 2002. [pdf]
High-speed Serial Interface 2013. Lect. 16 – Clock and Data Recovery 3 [http://tera.yonsei.ac.kr/class/2013_1_2/lecture/Lect16_CDR-3.pdf]
CC Chen. Why Hunting Jitter Happens in CDR: The Role of Input Jitter and Latency? [https://youtu.be/hPDielPsFgY]